Kurt Lewin’s Change Model
Introduction to Kurt Lewin’s Change Model
Kurt Lewin’s Change Model, developed by social psychologist Kurt Lewin in the 1940s, is a fundamental theory in the field of organizational change. It describes the process of change in three key stages: Unfreezing, Changing, and Refreezing. This model is acclaimed for its simplicity and effectiveness in understanding and managing change in organizations.
The Three Stages of the Model
- Unfreezing: This stage involves preparing the organization to accept that change is necessary. It encompasses breaking down the existing status quo and challenging current beliefs and behaviors. This can be achieved through increasing awareness of the need for change, creating a compelling message about the future, and engaging key stakeholders.
- Changing (or Transition): In this stage, the actual change occurs. It is where new ways of thinking, operating, and behaving are introduced. This phase often involves a period of confusion and transition, as people are learning and adapting to new systems and processes. Effective leadership and communication are critical to guide people through this stage.
- Refreezing: The final stage is about solidifying the new state after the change. This involves establishing stability once the changes have been made. Policies, procedures, and organizational culture are aligned with the new ways of working. This stage helps to ensure that the changes are sustained over time.
Application and Effectiveness
Lewin’s Change Model is widely used in various types of organizations. Its simplicity makes it easy to understand and apply, even in complex organizational settings. It emphasizes the importance of preparing for change, managing the transition effectively, and ensuring that change is lasting.
Challenges and Considerations
While the model provides a high-level framework, it may oversimplify the complexity of change management. Modern organizations often face rapidly changing environments where a more agile approach to change may be necessary. Additionally, the emotional and psychological aspects of change are not deeply explored in Lewin’s model.
Relevance in Modern Organizations
Despite its age, Lewin’s Change Model remains relevant. It serves as a foundation for many contemporary change management theories and practices. Its emphasis on the human side of change and the need for strong leadership and communication is particularly pertinent in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Conclusion
Kurt Lewin’s Change Model is a timeless tool that offers valuable insights into managing change. It underscores the importance of a structured and intentional approach to change, focusing on preparation, transition, and reinforcement to ensure successful and sustainable outcomes.
833 Comments
-
как купить диплом с проведением как купить диплом с проведением .
-
mental health support chatbot http://www.mental-health22.com .
-
где можно купить аттестат за 11 класс владивосток где можно купить аттестат за 11 класс владивосток .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в новосибирске купить аттестат за 11 класс в новосибирске .
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1771 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Пишите — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
цена винтовых свай ostankino-svai.ru .
-
купить диплом пту купить диплом пту .
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1774 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1035 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Пишите — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3892 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Открыть — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4956 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3166 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Открыть — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
диплом купить с проведением диплом купить с проведением .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс калининграде купить аттестат за 11 класс калининграде .
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов заказать https://www.arus-diplom22.ru .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс красноярск http://arus-diplom9.ru/ – купить аттестаты за 11 класс красноярск .
-
диплом купить в иркутске диплом купить в иркутске .
-
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://imgtube.ru/
-
диплом купить с занесением в реестр челябинск https://arus-diplom35.ru .
-
аттестат 11 класс купить уфа аттестат 11 класс купить уфа .
-
browse around here https://kikifinance.cc
-
you can look here https://sailor.my
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в уфе http://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с отличием http://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
-
сантехника логотип https://evropejskaya-santehnika.ru .
-
Sazrasi
Купить диплом под заказ вы можете через сайт компании. pakgovtnaukri.pk/companies/education-ua
-
купить диплом вуза с проводкой http://www.arus-diplom31.ru .
-
see this here https://extended-exchange.xyz/
-
mostbet sitio oficial mostbet sitio oficial
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов купить аттестат за 11 классов .
-
винлайн букмекерская контора бонус https://www.winlayne-fribet1.ru .
-
купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр .
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4604 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4329 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можно купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Diplomi_cnPi
Мы можем предложить документы университетов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 классов спб -
аттестат 11 класс 2017 купить аттестат 11 класс 2017 купить .
-
прогнозы на спорт бесплатно от профессионалов прогнозы на спорт бесплатно от профессионалов .
-
аттестат 11 классов купить москва аттестат 11 классов купить москва .
-
аппарат узи стоимость https://kupit-uzi-apparat8.ru .
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестр украина https://arus-diplom32.ru/ .
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3250 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Перейти — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4452 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом института образования — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3727 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Мы поможем — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2989 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Готовый диплом купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3496 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом документы — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
как купить аттестат за 11 как купить аттестат за 11 .
-
Sazrvgz
Заказать диплом на заказ в Москве можно через сайт компании. forestsnakes.teamforum.ru/viewtopic.php?f=28&t=7429
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2952 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
купить аттестат 11 цены дипломы челябинск ком https://www.arus-diplom23.ru .
-
плинко кз плинко кз
-
купить аттестат 11 классов цена купить аттестат 11 классов цена .
-
диплом с проводкой купить диплом с проводкой купить .
-
Priobresti diplom o visshem obrazovanii!_jnOr
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс в иркутске купить аттестаты за 11 класс в иркутске .
-
Diplomi_ciPi
Мы готовы предложить документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей РФ. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 класс краснодар -
высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр высшее образование купить диплом с занесением в реестр .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 в уфе купить аттестаты за 11 в уфе .
-
Thanks for the article. Here’s more on the topic https://mehelper.ru/
-
купить аттестат 10 11 класс вечерней школы купить аттестат 10 11 класс вечерней школы .
-
mostbet mostbet
-
Sazrbvj
Купить диплом можно используя сайт компании. rossensor.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=44335
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс 2021 год http://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
-
Danielphaps
We’re hastening for one’s help—some team by technicians which shall rapidly correct the results by the piping crisis at their apartment!
My fast action – the solution for decreasing one’s outlays for all following extensive repairs!
Test your speed with excellence by service right now! -
диплом с внесением в реестр купить диплом с внесением в реестр купить .
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4398 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Продажа дипломов о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 987 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Звоните — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4985 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3999 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом Россия — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
купить аттестат 11 классов санкт петербург купить аттестат 11 классов санкт петербург .
-
купить диплом о высшем образование https://arus-diplom7.ru .
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2422 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом университета — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1812 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом Россия — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3118 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом Киев — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4630 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом университета — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1909 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2596 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1040 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Открыть — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1350 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о профессиональном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
купить диплом вуза с проводкой http://arus-diplom35.ru/ .
-
melbet казино https://melbet1032.ru/
-
купить диплом магистра купить диплом магистра .
-
диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением купить .
-
Предлагаем ознакомиться остекление в Екатеринбурге сколько цена пластикового окна о теплом и холодном остеклении объектов. фасадное остекление .
-
Sazrghx
Приобрести диплом на заказ в столице возможно через официальный портал компании. old.workinginschools.com/employer/education-ua
-
купить диплом в томске купить диплом в томске .
-
Недавно обращался к профессиональному хакеру. Остался доволен. Заказывал услугу – Форумы хакеров
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижневартовске https://www.arus-diplom21.ru .
-
мостбет мостбет
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1443 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом вуза — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4115 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3923 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить учебный диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2125 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Пишите — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4125 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом с занесением — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр цена .
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3810 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о образовании недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
аттестат 11 класс 2014 купить аттестат 11 класс 2014 купить .
-
Lazroda
Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы можем предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным тарифам— dipmos.ru -
купить в чите диплом купить в чите диплом .
-
Sazrxjk
Купить диплом можно через сайт компании. teseygroup.ru/question/kupit-diplom-ofitsialno-i-bez-riska
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс краснодар купить аттестаты за 11 класс краснодар .
-
купить аттестат за 11 вечерней школы купить аттестат за 11 вечерней школы .
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1842 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4455 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить учебный диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1319 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4650 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На сайте — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
как купить аттестат за 11 класс сколько стоит как купить аттестат за 11 класс сколько стоит .
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2661 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом вуза — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
слушать и скачать музыку бесплатно в хорошем качестве mp3 в машину слушать и скачать музыку бесплатно в хорошем качестве mp3 в машину .
-
melbet официальный сайт melbet1038.ru
-
промокоды на melbet http://melbet1033.ru
-
melbet отзывы melbet1037.ru
-
диплом купить с проведением диплом купить с проведением .
-
купить проведенный диплом высокие купить проведенный диплом высокие .
-
купить диплом о высшем образовании реестр купить диплом о высшем образовании реестр .
-
купить диплом в перми купить диплом в перми .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс в мурманске купить аттестаты за 11 класс в мурманске .
-
купить диплом с проводкой моих купить диплом с проводкой моих .
-
пластиковые окна москва пластиковые окна москва .
-
melbet registration melbet registration
-
купить проведенный диплом одно купить проведенный диплом одно .
-
купить диплом среднее специальное образование купить диплом среднее специальное образование .
-
try these out
sky kingdom aviation -
мелбет регистрация https://melbet1034.ru
-
как купить диплом проведенный как купить диплом проведенный .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в кропоткине купить аттестаты за 11 классов в кропоткине .
-
Diplomi_caPi
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат 11 классов в челябинске -
It is always interesting to see how people find different approaches to solving various tasks. Sometimes you encounter similar situations in completely unrelated areas, and the method of overcoming obstacles largely determines the end result.
By the way, it reminded me of the importance of being prepared for unforeseen difficulties, especially in winter on the road. In such cases, snow chains become a real salvation, allowing you to confidently move forward even on the most difficult sections.
-
где купить аттестат за 11 класс в оренбурге где купить аттестат за 11 класс в оренбурге .
-
ссылка на кракен зеркало – как зайти на кракен, ссылка на кракен
-
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании с занесением в реестр .
-
как купить аттестат 11 класса как купить аттестат 11 класса .
-
диплом внесенный в реестр купить диплом внесенный в реестр купить .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске https://www.arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестат за 11 класс в красноярске .
-
диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить .
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2205 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3291 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом нового образца — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1509 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Открыть — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1783 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Уточнить здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
kraken тор – kraken darknet tor, кракен даркнет тор
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1199 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом бакалавра купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
диплом купить в хабаровске диплом купить в хабаровске .
-
kraken onion ссылка – kraken тор, ссылка на кракен
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестры купить диплом с занесением в реестры .
-
аттестат за 11 класс купить ярославль аттестат за 11 класс купить ярославль .
-
аттестат за 11 класс купить ярославль аттестат за 11 класс купить ярославль .
-
корочка аттестата за 11 класс купить корочка аттестата за 11 класс купить .
-
кракен онион – kraken onion, вход на кракен даркнет
-
можно ли купить аттестаты за 11 можно ли купить аттестаты за 11 .
-
кракен официальный сайт – kraken тор, зайти на кракен даркнет
-
кракен даркнет – кракен darknet, kraken tor
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1880 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
По ссылке — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3950 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом купить в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4565 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом института — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4411 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4462 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4395 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4025 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом колледжа купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в новосибирске купить аттестаты за 11 классов в новосибирске .
-
kraken onion market – зайти на кракен даркнет, рабочая ссылка на кракен
-
купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 купить аттестат в красноярске за 11 .
-
ссылка на кракен – кракен сайт, кракен darknet
-
кракен даркнет ссылка – актуальная ссылка на кракен, kraken tor
-
кредитная карта переводы без процентов кредитная карта переводы без процентов .
-
автокредит на авто автокредит на авто .
-
telegram_bpot
Накрутка живых подписчиков в ТГ канал дешево вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3103332-nakrutka-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-deshevo-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-v-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов в чите arus-diplom24.ru .
-
Diplomi_hxPi
Мы можем предложить документы университетов, которые находятся в любом регионе РФ. Заказать диплом ВУЗа:
как купить аттестат за 11 -
купить проведенный диплом спб http://arus-diplom32.ru/ .
-
Sazrffh
Приобрести диплом возможно через сайт компании. lmd100.lk/2025/07/08/kupit-diplom-oficialno-i-bez-riska-148
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в новокузнецке купить аттестат за 11 класс в новокузнецке .
-
dizainerskie kashpo_yaOr
стильные цветочные горшки купить стильные цветочные горшки купить .
-
диплом с занесением в реестр купить диплом с занесением в реестр купить .
-
купить диплом с реестром киев купить диплом с реестром киев .
-
аттестат за 11 класс купить аттестат за 11 класс купить .
-
слушать музыку бесплатно онлайн в хорошем качестве слушать музыку бесплатно онлайн в хорошем качестве .
-
Cazrdpf
Мы можем предложить дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам. Купить диплом в Нижнекамске — kyc-diplom.com/geography/nizhnekamsk.html
-
купить аттестат 11 класс 2006 год купить аттестат 11 класс 2006 год .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем тагиле купить аттестат за 11 класс в нижнем тагиле .
-
Kypit diplom instityta!_cgOr
диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр купить .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в реестр екатеринбург купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в реестр екатеринбург .
-
купить диплом с реестром в москве купить диплом с реестром в москве .
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург .
-
аттестат за 11 класс купить в екатеринбурге аттестат за 11 класс купить в екатеринбурге .
-
купить аттестат 11 классов цена купить аттестат 11 классов цена .
-
диплом купить с проведением диплом купить с проведением .
-
find more https://web-jaxxliberty.com/
-
mostbet com http://mostbet4079.ru
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в минске купить аттестат за 11 класс в минске .
-
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в кемерово купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в кемерово .
-
купить диплом в вологде купить диплом в вологде .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 отзывы купить аттестаты за 11 отзывы .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс купить аттестаты за 11 класс .
-
mostbet uz skachat kompyuter https://mostbet4072.ru/
-
Sazrayc
Заказать диплом вы имеете возможность через сайт компании. zador.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=4113&sid=e87418e24740da22f4561c0427720448
-
Danielphaps
Pioneering new capsules designed for powerful climaxes – more intense as well as even more potent feelings!
One-of-a-kind innovation – modern progress within medical science!
Completely risk-free as well as very efficient – enhances libido along with boosts sexual firmness!
Boost individual climax amount instantly! -
купить диплом среднее образование купить диплом среднее образование .
-
купить диплом с реестром спб купить диплом с реестром спб .
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4519 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о образовании недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3927 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом об окончании института — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3611 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1004 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом университета — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1094 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можна купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
steelersfanpsype
-
купить диплом с проводкой одно купить диплом с проводкой одно .
-
как купить диплом занесенный в реестр как купить диплом занесенный в реестр .
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3895 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Диплом сколько стоит — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
mostbet ilova http://www.mostbet4080.ru
-
Перейти на сайт kraken вход
-
Lazrxnf
Заказать диплом института!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным тарифам— uuirb.ru -
ссылка на сайт https://kra36at.at
-
купить аттестат в ульяновске купить аттестат в ульяновске .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс смоленск http://arus-diplom23.ru .
-
ссылка на сайт кракен официальная ссылка
-
dizainerskie kashpo_acOl
стильные горшки для цветов купить стильные горшки для цветов купить .
-
click here for info jax wallet
-
top article jaxx liberty
-
telegram_wcot
Накрутка просмотров Телеграм бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1284903-nakrutka-prosmotrov-telegram-besplatno-top-19-servisov-2025-goda-preimushestva Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4332 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Пишите нам — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 2229 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1231 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Открыть — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3328 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Куплю диплом о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 915 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1105 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
additional reading https://jaxx-liberty.net
-
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 3570 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом Москва — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 4430 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о высшем образовании в Москве — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
где купить диплом с реестром где купить диплом с реестром .
-
аттестат за 11 класс купить москва аттестат за 11 класс купить москва .
-
купить диплом в барнауле купить диплом в барнауле .
-
dizainerskie kashpo_anOl
дизайнерские цветочные горшки дизайнерские цветочные горшки .
-
аттестат 11 купить аттестат 11 купить .
-
аттестаты купить в москве за 11 класс аттестаты купить в москве за 11 класс .
-
Lazrudq
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам— poluchidiplom.com -
купить диплом вуза с реестром купить диплом вуза с реестром .
-
Diplomi_iaPi
Мы предлагаем документы учебных заведений, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестаты за 11 класс московская область -
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2006 года https://arus-diplom24.ru .
-
Sazrufp
Купить диплом на заказ вы можете через сайт компании. 1stroitelny.kz/faq/show/id/686cd70e757d2759eb29f593.html
-
over at this website https://lumi-wallet.io
-
где купить аттестат за 11 класс в кемерово где купить аттестат за 11 класс в кемерово .
-
you can find out more https://sollet-wallet.io
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в новосибирске цена купить аттестаты за 11 классов в новосибирске цена .
-
Bistro priobresti diplom ob obrazovanii!_pxOr
можно купить легальный диплом можно купить легальный диплом .
-
купить легальный диплом колледжа купить легальный диплом колледжа .
-
где купить аттестат 11 классов в кургане где купить аттестат 11 классов в кургане .
-
melbet apps https://melbet1039.ru/
-
сколько стоит купить диплом о высшем образовании https://arus-diplom6.ru/ .
-
купить диплом без занесения в реестр купить диплом без занесения в реестр .
-
Diplomi_riPi
Мы предлагаем документы учебных заведений, которые находятся на территории всей России. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
купить аттестат за 11 класс в сургуте -
купить диплом где можно купить диплом где можно .
-
here are the findings Lumi online
-
reference https://lumi-wallet.io
-
страница kraken вход
-
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальностьУже более 1463 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Где можно купить диплом — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
-
найти это платёжные решения для форекс
-
пояснения аренда авто без водителя минск
-
продолжить Купить ип
-
ссылка на сайт вбаксы код фортнайт
-
можно проверить ЗДЕСЬ https://weekpay.ru
-
Смотреть здесь кра сайт
-
купить аттестаты 11 купить аттестаты 11 .
-
dizainerskie kashpo_jzPa
кашпо стильные кашпо стильные .
-
опубликовано здесь https://kinogo.blue/filmy/2655-seks-po-druzhbe.html
-
купить диплом с проведением купить диплом с проведением .
-
купить проведенный диплом о высшем образовании купить проведенный диплом о высшем образовании .
-
диплом купить медицинский http://www.arus-diplom7.ru/ .
-
аттестат за 11 класс купить архангельск аттестат за 11 класс купить архангельск .
-
Sazrszw
Приобрести диплом возможно через официальный портал компании. empleo.infosernt.com/employer/education-ua
-
диплом купить с занесением в реестр отзывы http://arus-diplom33.ru .
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов в челябинске https://www.arus-diplom25.ru .
-
купить диплом вуза с проводкой http://www.arus-diplom33.ru/ .
-
я купил проведенный диплом я купил проведенный диплом .
-
купить аттестат за 10 11 классы купить аттестат за 10 11 классы .
-
купить аттестат в украине об окончании 11 класса https://arus-diplom22.ru/ .
-
mp 3 mp 3 .
-
купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр купить диплом пту с занесением в реестр .
-
как получить промокод на мелбет как получить промокод на мелбет
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс в оренбурге купить аттестат за 11 класс в оренбурге .
-
MichaelSkire
This article reminds homeowners that small, consistent maintenance can prevent costly damage. The practical guidance is easy to follow and very motivating. I also found some helpful repair techniques that fit well with these tips and helped me keep everything under control.
-
подробнее kra37 at
-
Lazrkxb
Заказать диплом любого университета!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам— mplzt.ru -
Cazruhp
Получить диплом о высшем образовании поспособствуем. Купить диплом Новосибирск – diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-novosibirsk
-
Diplomi_pcPi
Мы предлагаем документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа:
купить аттестат за 11 классов в екатеринбурге -
купить аттестаты в москве за 11 классов купить аттестаты в москве за 11 классов .
-
диплом фельдшера купить диплом фельдшера купить .
-
диплом высшего образования проведенный купить диплом высшего образования проведенный купить .
-
купить диплом о высшем образовании с реестром купить диплом о высшем образовании с реестром .
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов в иваново купить аттестат за 11 классов в иваново .
-
Sazrjja
Заказать диплом под заказ в Москве возможно используя сайт компании. newsstatix.com/kupit-diplom-oficialno-i-bez-riska-193
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в украине http://arus-diplom34.ru .
-
как купить легально диплом о высшем образовании как купить легально диплом о высшем образовании .
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов в ростове купить аттестат за 11 классов в ростове .
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов в череповце https://arus-diplom23.ru/ .
-
купить аттестаты 11 arus-diplom9.ru – купить аттестаты 11 .
-
купить диплом о среднем специальном купить диплом о среднем специальном .
-
я купил проведенный диплом я купил проведенный диплом .
-
купить диплом с проводкой моего купить диплом с проводкой моего .
-
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2016 года купить аттестат за 11 класс 2016 года .
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов москва купить аттестат за 11 классов москва .
-
можно ли купить аттестаты за 11 класс https://arus-diplom22.ru .
-
dizainerskie kashpo_gtoi
оригинальные горшки для цветов купить оригинальные горшки для цветов купить .
-
купить аттестат 11 класс купить аттестат 11 класс .
-
Lazrbtm
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по приятным тарифам— diplomdoc.ru -
telegram_fxot
100 подписчиков в Телеграм вот статья: https://dtf.ru/top-smm/3144892-kak-nabrat-100-podpischikov-v-telegram-top-27-proverennyh-servisov-2025-goda-novyi-reiting Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестр чита https://arus-diplom35.ru/ .
-
диплом настоящий купить с занесением в реестр http://www.arus-diplom33.ru/ .
-
Diplomi_noPi
Мы предлагаем документы учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей РФ. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
аттестат за 11 классов купить -
где купить аттестат за 10 11 где купить аттестат за 10 11 .
-
купить диплом о высшем купить диплом о высшем .
-
купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением в реестр купить аттестаты за 11 класс с занесением в реестр .
-
где купить аттестат 11 классов в кургане где купить аттестат 11 классов в кургане .
-
Cazrrok
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по разумным ценам. Купить диплом автомеханика — kyc-diplom.com/diplomy-po-professii/diplom-avtomehanika.html
-
как купить аттестат 11 классов как купить аттестат 11 классов .
-
можно купить легальный диплом http://arus-diplom31.ru .
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестр новокузнецке купить диплом с занесением в реестр новокузнецке .
-
how can i stimulate hair growth can prednisone affect kidneys prednisone price walmart can you drink alcohol with short term prednisone how many feet of intestines in a human body
-
Приглашаем узнать остекление в Екатеринбурге остекление окон о теплом и холодном остеклении объектов. остекление балконов и лоджий .
-
диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить .
-
Sazrypj
Заказать диплом вы имеете возможность через сайт компании. vira-ss.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=1049
-
диплом купить реестр [url=http://www.arus-diplom32.ru]диплом купить реестр[/url] .
-
MichaelSkire
This article breaks down place improvement into simple tasks that anyone can manage. The motivation to start small is helpful for beginners. I paired this with a few useful repair strategies that complemented the advice nicely, improving my results.
-
купить аттестат за 11 классов госзнак купить аттестат за 11 классов госзнак .
-
EarnestarEts
Мы https://avtosteklavoronezh.ru/ предлагаем широкий спектр услуг для автовладельцев — от покупки новых автомобилей до удобного обмена и быстрого выкупа вашего старого автомобиля. Наша команда профессионалов гарантирует честную оценку, оперативное снятие с учета и быстрое получение расчета прямо на месте всего за 10–20 минут!
-
Cosmetology clinic Marbella Cosmetology clinic Marbella .
-
look at more info
toast wallet xrp -
OLaneNum
For newest information you have to go to see internet and on web I found this site as a finest site for newest updates.
Покер онлайн -
maorou_k8m maorou k8m
-
article source
toast wallet website -
за сколько можно купить аттестат за 11 классов за сколько можно купить аттестат за 11 классов .
-
Danielphaps
The World Games announcement articulated profound anguish for this misfortune and provided genuine condolences to the competitor’s family, associates, and the full Orienteering Community. Our sentiments linger with those touched by this event.
https://edasmak.blogspot.com/2025/04/qualities-of-chef.html -
купить аттестат 11 классов в красноярске http://arus-diplom21.ru/ .
-
купить диплом переводчика http://arus-diplom8.ru .
-
Dichaelned
Hello there, You have done an excellent job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this website.
https://telegra.ph/CHomu-sklo-fari-zhovt%D1%96ye-shvidshe-na-sonyachn%D1%96j-storon%D1%96-avto-08-11 -
медицинский косметолог медицинский косметолог .
-
Robertrourl
РњРЅРµ импонирует, РєРѕРіРґР° материалы делают СѓС…РѕРґ Р·Р° РґРѕРјРѕРј доступным, без жаргона Рё нереалистичных ожиданий. Рта статья именно такая. Р’ сочетании СЃ эффективными DIY советами, которые СЏ недавно нашёл, РјРЅРµ удалось завершить проекты, которые откладывал. Воодушевляет видеть практичные Рё мотивирующие советы.
-
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в мурманске купить диплом с занесением в реестр в мурманске .
-
dizainerskie kashpo_utmn
креативные горшки для цветов купить dizaynerskie-kashpo-nsk.ru .
-
tgram_bkot
Накрутка подписчиков в тик токе бесплатно – ТОП-50 лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1274797-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tik-toke-besplatno-top-50-luchshih-servisov Лучшие платформы для набора и накрутки
-
EddBfJabs
cannaexpress-market-mirror.cc
-
Dichaelned
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
-
FobertkeypE
Hello! I understand this is sort of off-topic but I had to ask. Does running a well-established blog such as yours require a large amount of work? I’m brand new to writing a blog however I do write in my diary on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I can share my personal experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any kind of ideas or tips for new aspiring bloggers. Thankyou!
-
OLaneNum
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable knowledge concerning unpredicted feelings.
-
LhaneNum
Hi there colleagues, how is all, and what you would like to say regarding this paragraph, in my view its genuinely remarkable in favor of me.
Seattle limo rates -
https://crazy-time.games/ The official Crazy Time website offers a complete guide to Evolution’s live money wheel game. Learn the rules, explore bonus rounds, discover strategies, track results, and find trusted online casinos to play Crazy Time worldwide.
-
ограждение пандуса из нержавеющей стали Перила деревянные – это универсальное решение, которое подходит для различных типов лестниц и интерьеров. Они могут быть изготовлены из различных пород дерева, таких как сосна, дуб, бук или ясень, и иметь различную отделку. }
-
где оформить визу в китай Как оформить визу в Китай для россиян: Пошаговая инструкция для успешного результата. Оформление визы в Китай для россиян требует внимательности и соблюдения определенных правил. Подготовьте необходимый пакет документов, включая загранпаспорт, фотографии, анкету и подтверждение брони отеля и авиабилетов. Следуйте инструкциям визового центра или консульства, и ваш запрос будет рассмотрен в кратчайшие сроки.
-
telegram_dwot
Купить живых подписчиков в ТГ вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1176242-kupit-podpischikov-v-tg-kanal-zhivyh-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-shemy Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
-
Brandonbow
I came to Asia International School – Girls Section with hopes of academic growth, new friendships, and a future built on opportunity. But what I’ve encountered in Riyadh is something no school brochure warned about. There are moments where my thoughts become fragmented, my emotional state shifts suddenly, and I feel watched even in empty hallways. These episodes are not rare. They are structured. Predictable. I began to realize I was being interfered with — not socially, but neurologically.
What’s happening isn’t abstract. It’s not paranoia. It’s the result of deliberate interference by Saudi internal intelligence services, military-affiliated signal control divisions, and units tied to the Ministry of Interior. This is not education under pressure — it is behavior modification under cover of schooling. There is an invisible infrastructure here that manipulates mental states through remote influence. And no one inside these institutions will talk about it.
I’ve said nothing until now because the consequences of speaking are obvious. You are labeled unstable. You lose your place. You become a target twice over. If I had known what studying in this country actually entailed, I would have never applied. Now I write this so that the illusion can fracture — even if only slightly.
-
кайт хургада Кайтсёрфинг Египет: Наслаждайтесь ветром и волнами в райском уголке. Египет – это рай для кайтсерферов. Здесь вас ждут километры песчаных пляжей, кристально чистая вода и стабильный ветер. Катайтесь в свое удовольствие и наслаждайтесь красотой Красного моря.
-
https://kazan.land/ Озеро Кабан: Жемчужина Казани и Место Легенд Озеро Кабан – одно из самых живописных мест Казани, окруженное парками и скверами. Это место, где можно отдохнуть от городской суеты, насладиться красотой природы и узнать о легендах, связанных с озером. По легенде, на дне озера спрятаны сокровища Казанского ханства. Вы можете прогуляться по набережной, покататься на лодке или катамаране, а также посетить расположенные рядом музеи и театры.
-
https://t.me/elekt_riki Жизнь без перебоев: Надежное электроснабжение – залог вашего комфорта.
-
essay writier College Admission Essay Specialists: Your Path to Acceptance Navigate the competitive landscape of college admissions with our expert essay writing services. We help you craft compelling narratives that showcase your unique qualities.
-
OLaneNum
For quick, reliable JPEG-to-JPG conversions, turn to JPEGtoJPGHero.com. This online utility requires no sign-up or payment—just a fast, ad-free process in a clean interface. Drag and drop images into the upload box, or click to browse. The server handles conversion without sacrificing image clarity, working behind the scenes while you see a progress bar track each file. Multiple images convert in a single batch, cutting down repetitive clicks. Download links pop up as soon as the job finishes, letting you save updated JPG files in seconds. The browser-based design means the tool functions equally well on Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Privacy remains a priority: every uploaded image is deleted automatically after conversion, and no user data gets stored permanently. Use cases range from preparing photography portfolios to formatting images for email attachments. By keeping features simple and focusing on performance, JPEGtoJPGHero.com ensures that converting JPEG images to the widely accepted JPG format never feels complicated or time-consuming.
JPEGtoJPGHero.com -
gorshok s avtopolivom_cxst
кашпо с системой полива kashpo-s-avtopolivom-kazan.ru .
-
экскурсии по казани Остров-Град Свияжск: Духовный Центр и Историческое Наследие Остров-град Свияжск – это уникальный исторический и культурный памятник, расположенный на острове в месте слияния рек Свияги и Волги. Это место, где история переплетается с духовностью, где можно увидеть древние храмы и монастыри, а также узнать о жизни и культуре русского народа. На острове расположены многочисленные памятники архитектуры, включая Успенский собор, Троицкую церковь и другие исторические здания. Вы сможете прогуляться по живописным улочкам, насладиться красотой природы и почувствовать атмосферу умиротворения.
-
Всем привет!
Меня зовут Лазарь и я обожаю смотреть онлайн мультсериал Южный Парк на сайте https://southpark-online.com
Там много интересных серий, которые Вам понравятся.
Присоединяйтесь! -
проверить сайт трипскан сайт вход
-
IsmaelKnifs
What’s up to all, it’s really a fastidious for me to visit this site, it contains valuable Information.
биткоин обменник на российский счет с круглосуточной поддержкой онлайн -
FobertkeypE
PNGtoJPGHero leverages cutting-edge browser-based image processing to transform PNG files into high-quality JPGs without installing any external software. Its core engine applies adaptive compression, intelligently balancing image fidelity with reduced file size. This makes it ideal for web developers optimizing assets, marketers preparing images for campaigns, or anyone managing storage constraints. The conversion pipeline supports simultaneous multi-file processing, ensuring speed even with large batches. Built with responsive design principles, the interface adapts seamlessly to desktop, tablet, and mobile screens. Robust privacy protocols ensure that uploaded images are encrypted in transit and purged from the server shortly after processing. By combining lightweight front-end performance with efficient server-side handling, PNG to JPG Hero delivers consistent results in under a second per image. It’s a precise, reliable, and secure solution for converting images at scale or on the go.
PNGtoJPGHERO -
https://kazan.land/ Остров-Град Свияжск: Духовный Центр и Историческое Наследие Остров-град Свияжск – это уникальный исторический и культурный памятник, расположенный на острове в месте слияния рек Свияги и Волги. Это место, где история переплетается с духовностью, где можно увидеть древние храмы и монастыри, а также узнать о жизни и культуре русского народа. На острове расположены многочисленные памятники архитектуры, включая Успенский собор, Троицкую церковь и другие исторические здания. Вы сможете прогуляться по живописным улочкам, насладиться красотой природы и почувствовать атмосферу умиротворения.
-
IsmaelKnifs
Frustrated by WebP files that won’t open on certain devices or platforms? webptojpghero.com provides a quick, straightforward fix. This online tool instantly converts any WebP image into a widely compatible JPG, ready for use in emails, websites, or printed materials. The process is effortless: upload your file, let the conversion engine work, and download your result — all in under a minute. You can process individual files or multiple images at once, making it perfect for both occasional use and high-volume projects. Behind the simple interface is a sophisticated image-processing core that ensures vibrant colors and clear details, even at smaller file sizes. Everything happens securely, with encryption protecting your uploads and automatic deletion safeguarding your privacy. Whether on desktop, tablet, or mobile, WebP to JPG Hero ensures your images are ready for universal access without hassle.
WebP to JPG Converter -
https://kitehurghada.ru/ Кайт обучение Хургада Кайт Хургада Солнце ласкает кожу, ветер играет в волосах, а бескрайняя гладь Красного моря манит своей глубиной. Хургада – это место, где мечты о полете над волнами становятся реальностью. Кайтсёрфинг здесь – это не просто спорт, это образ жизни, это свобода и адреналин в каждой секунде. Кайт Школа Хургада Первые шаги в мир кайтсёрфинга могут быть непростыми, но опытные инструкторы кайт школы в Хургаде помогут вам освоить азы и почувствовать уверенность на доске. Индивидуальный подход, современное оборудование и безопасные условия обучения сделают ваш опыт незабываемым. Кайт Сафари Хургада Для тех, кто жаждет приключений и новых горизонтов, кайт сафари в Хургаде – это идеальный выбор. Отправьтесь в путешествие по живописным островам и лагунам, где ветер всегда дует в вашу пользу. Новые споты, новые знакомства и море впечатлений гарантированы. Кайтсёрфинг Хургада Хургада – это настоящий рай для кайтсёрферов. Здесь вы найдете все, что нужно для идеального катания: стабильный ветер, теплое море и разнообразие спотов для любого уровня подготовки. Откройте для себя мир кайтсёрфинга в Хургаде! Кайт Школа Египет Египет – это не только пирамиды и фараоны, но и прекрасные возможности для кайтсёрфинга. Кайт школы в Египте предлагают обучение с нуля до продвинутого уровня. Опытные инструкторы, современные методики и безопасные условия сделают ваш опыт обучения приятным и эффективным. Кайтсёрфинг Египет Кайтсёрфинг в Египте – это возможность совместить активный отдых с познавательными экскурсиями. После дня, проведенного на воде, вы можете отправиться исследовать древние храмы и гробницы. Египет – это страна, где история и современность переплетаются в удивительном танце. Кайт Обучение Хургада Мечтаете научиться управлять кайтом и скользить по волнам? Кайт обучение в Хургаде – это ваш шанс! Квалифицированные инструкторы помогут вам освоить технику безопасности, управление кайтом и уверенно стоять на доске. Кайт Обучение Египет Египет предлагает широкий выбор школ и инструкторов по кайтсёрфингу. Независимо от вашего уровня подготовки, вы найдете подходящую программу обучения. Начните свое кайт-приключение в Египте и откройте для себя мир адреналина и свободы!
-
telegram_utot
Купить подписчиков в ТГ канал живых вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1175987-nakrutit-zhivyh-podpischikov-v-tg-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-moi-shemy Только проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
-
скачать игры без торрента Скачать игры по прямой ссылке: Мгновенный доступ к игровым мирам Прямые ссылки – это как личный экспресс-маршрут к игровому контенту. Никаких посредников, сложных процедур или томительного ожидания загрузки. Мгновенный доступ к желаемой игре – вот что делает этот способ скачивания таким привлекательным для современных геймеров. Это оптимальный выбор для тех, кто ценит свое время и стремится к максимальной эффективности.
-
Запчасти для стиральной машины LG WD-10360ND Запчасти для стиральной машины Vestel WM1034E: Долговечность и надежность – визитная карточка техники Vestel. Не позволяйте мелким поломкам прервать привычный ритм жизни, замените изношенные детали и наслаждайтесь безупречной работой вашей стиральной машины.
-
https://igrozavod.ru/ Альтернативы торрентам: Мир без границ Не ограничивайтесь устаревшими способами получения игр. Исследуйте мир альтернативных источников, предлагающих высокое качество, безопасность и удобство. Откройте для себя новые возможности и наслаждайтесь геймингом без ограничений.
-
GichardCaw
Attractive section of content. I simply stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to say that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your weblog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I fulfillment you get admission to consistently fast.
-
перманентные брови севастополь Сделать брови в Севастополе: Найдите своего мастера. Лучшие бровисты города готовы воплотить ваши мечты об идеальных бровях в реальность.
-
взлом ватсап Мы помогаем взломать: Социальные сети. Разберитесь в хитросплетениях личных связей, раскройте тайны, скрытые за аватарками. Получите полное представление о жизни интересующего вас человека, его окружении и намерениях.
-
https://t.me/s/zerkalo1x Зеркало 1xbet: ваш ключ к стабильному заработку. Больше не нужно искать способы обхода блокировок – наше зеркало обеспечит вам бесперебойный доступ к платформе. Делайте ставки, выигрывайте и получайте удовольствие от игры, не беспокоясь о технических проблемах.
-
dizainerskie kashpo_aepl
дизайнерские горшки для комнатных растений http://www.dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru .
-
здоровье красота Уход: инвестиция в будущее вашей кожи. Регулярные процедуры, направленные на увлажнение, питание и защиту, помогут вам сохранить молодость и красоту на долгие годы.
-
Dichaelned
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article author for your blog. You have some really good articles and I believe I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d really like to write some articles for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please send me an email if interested. Regards!
-
nik_ieot
Для продвижения через ботов очень помог блог https://vc.ru/niksolovov всё показано.
-
tripscan войти Tripscan: Откройте для себя мир, полный новых горизонтов и впечатлений. Наша платформа предлагает индивидуальный подход к планированию путешествий, позволяя подобрать идеальные варианты проживания, перелетов и развлечений, соответствующие вашим предпочтениям и бюджету.
-
tripscan вход Трипскан топ: Лучшие направления и выгодные предложения ждут вас.
-
лучшая жизнь Лучшая жизнь: Стремитесь к гармонии во всех сферах жизни: личной, профессиональной, духовной. Развивайте свои таланты, окружайте себя любящими людьми, занимайтесь любимым делом и не бойтесь мечтать о большем. Лучшая жизнь – это не цель, а процесс постоянного самосовершенствования.
-
Домики на берегу Рыбалка в Карелии: Забудьте о городской суете и отправляйтесь на рыбалку в Карелию. Здесь вы сможете поймать лосося, форель, хариуса и другие ценные виды рыб. Рыбалка в Карелии – это не просто хобби, это страсть, это способ почувствовать себя частью природы.
-
RalphPor
I appreciate how this write-up focuses on real-life situations rather than abstract concepts. It’s always a pleasure to read something hands-on. While going through the post, I was reminded of a set of reliable house solutions that align with many of the ideas you mentioned. Whether it’s fixing a leaky tap or organizing space better, having multiple sources of trustworthy information really makes a difference.
-
tripscan личный кабинет Tripscan: Путешествуйте свободно, исследуйте мир без границ. Погрузитесь в атмосферу приключений, откройте для себя новые культуры и создайте незабываемые воспоминания. Мы поможем вам спланировать идеальное путешествие, учитывая ваши предпочтения и бюджет.
-
GichardCaw
Greetings! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My blog discusses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you’re interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Great blog by the way!
http://brandwatches.com.ua/sklo-fary-ta-lakove-pokryttya-perevahy.html -
gorshok s avtopolivom_ezSi
кашпо с автополивом кашпо с автополивом .
-
недвижимость в Турции Экономика Турции: Тенденции, прогнозы, инвестиции, ключевые отрасли, развитие бизнеса и новые возможности для предпринимателей
-
https://t.me/Foka_Doka_SPb 3D печать: Быстрое прототипирование и создание уникальных изделий
-
midjourney ИИ для Создания: Инструмент или Муза?
-
https://t.me/provrf_ru Купить VRF: Инвестиция в Будущее Приобретение VRF системы – это инвестиция в будущее вашего дома или бизнеса. Эти системы позволяют существенно снизить энергопотребление и затраты на электроэнергию, обеспечивая при этом максимальный комфорт.
-
Антижучок Видеокамеры наблюдения: Глаза, которые никогда не спят Современные видеокамеры наблюдения предлагают широкий спектр функций, от записи в высоком разрешении до удаленного доступа через интернет. Они становятся неотъемлемой частью систем безопасности для домов, офисов и предприятий.
-
Danielphaps
We’re prepared to solve the problem — a capable team poised to handle your plumbing emergency and bring back peace in your home!
Our fast assistance facilitates – lower the requirement for expensive significant restorations in the future.
Explore our swift and excellent service – right now! -
LhaneNum
Hi to all, how is the whole thing, I think every one is getting more from this web site, and your views are nice in favor of new visitors.
https://polygraph.od.ua/chomu-sklo-fary-z-uv-zakhystom-tse-must-have.html -
купить VRV Купить VRV: Индивидуальный Подход к Климату VRV системы обеспечивают индивидуальный подход к созданию комфортного климата в каждом помещении. Благодаря возможности независимой регулировки температуры, вы можете создать идеальные условия для работы, отдыха или проживания.
-
Brianwix
<a href=http://www.rlwedding.com/les-meilleures-machines-a-sous-pour-jouer-avec-de-2/http://www.rlwedding.com/les-meilleures-machines-a-sous-pour-jouer-avec-de-2/
-
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I do not know who you are but certainly you are going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
-
доставка товаров из Китая грузоперевозки из Китая в Россию
-
английский для взрослых Уроки английского для взрослых: Интерактивное обучение Наши уроки английского языка для взрослых проходят в интерактивной и увлекательной форме. Мы используем современные методики обучения, чтобы сделать процесс изучения языка интересным и эффективным.
-
Dichaelned
ゼントレーダーで始める|Zenブログで深める賢い投資ライフ
最近、投資をよりシンプルに、そして効率的に始めたいと考える人々の間で注目されているのが「ゼントレーダー(Zentrader)」です。登録から取引までが非常にスムーズで、初心者にもわかりやすい設計が魅力です。
特に「Zenブログ」では、投資に関する基本知識から実践的な取引戦略まで、幅広い情報が発信されており、学びながら実践できる環境が整っています。日々のマーケット動向やトレンドも分かりやすく解説されているため、忙しい人でも効率よく情報収集が可能です。
さらに、投資初心者がつまずきやすいポイントやリスク管理の方法についても、https://social-consulting.jp/ にて実践的なアドバイスが紹介されています。投資を「感覚」ではなく「戦略」として考えたい方におすすめです。
-
DavidWef
Reading through this post highlights how small, consistent efforts can prevent bigger problems around the house. The straightforward guidance is exactly what many beginners need. I’ve been using some supportive repair suggestions lately, and they work well alongside these tips to keep everything in order. It resonates with my own experience of how consistent, step‑by‑step improvements create a much more comfortable and reliable living space.
-
Your posts provide a clear, concise description of the issues.
-
telegram_gsot
Накрутка подписчиков в ТГ бесплатно вот статья: https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1453520-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-tg-besplatno-top-25-servisov-2025-goda-lichnyi-vybor nолько проверенные бесплатные и платные способы получить больше подписчиков.
-
Привет, кто заходил на Kraken через TOR сегодня?
krakr.cc|
Kraken работает через krakr.cc, проверил только что|
Подскажите, кто пользуется Kraken? Официальный сайт krakr.cc|
Захожу на Kraken только через krakr.cc, сайт стабильный|
Kraken официальный сайт krakr.cc, всегда через
TOR|
Кто знает, krakr.cc это рабочее зеркало
Kraken?|
Kraken грузится через krakr.cc без проблем|
Привет всем, кто пользуется Kraken через
TOR?|
Kraken работает отлично, официальный сайт krakr.cc|
Захожу на Kraken через TOR и krakr.cc, всё ок|
Kraken доступен по krakr.cc без перебоев|
Кто-нибудь использует Kraken сейчас?
krakr.cc|
Kraken официальный сайт работает через krakr.cc|
krakr.cc лучший сайт для входа
на Kraken|
TOR и krakr.cc – стабильный вход на Kraken|
Kraken через krakr.cc открыт сегодня|
Проверил krakr.cc – Kraken работает быстро|
Кто заходит на Kraken через TOR
браузер?|
Kraken работает 24/7 через krakr.cc|
Kraken krakr.cc загружается моментально|
krakr.cc это официальный сайт Kraken|
Захожу на Kraken через TOR всегда|
Kraken грузится быстро через krakr.cc|
Kraken работает через TOR браузер|
Kraken официальный сайт krakr.cc сегодня|
Кто знает, krakr.cc актуален сейчас?|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт без блокировок|
TOR и Kraken krakr.cc – проверено|
Kraken krakr.cc лучший выбор|
Kraken работает через TOR без проблем|
krakr.cc официальный сайт Kraken|
Kraken krakr.cc грузится мгновенно|
Kraken доступен через krakr.cc|
Kraken официальный сайт открыт|
krakr.cc стабильное зеркало Kraken|
Kraken через TOR работает стабильно|
krakr.cc всегда актуальная ссылка|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасный вход|
Kraken krakr.cc сегодня без лагов|
Kraken через krakr.cc работает отлично|
Кто проверял krakr.cc сегодня?|
Kraken krakr.cc быстро грузится|
Kraken официальный сайт всегда доступен|
Kraken krakr.cc работает моментально|
Kraken через TOR браузер открыт|
krakr.cc для входа на Kraken|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт доступен|
Kraken официальный сайт krakr.cc активен|
krakr.cc заходите через TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда рабочий|
Kraken официальный сайт без блоков|
Kraken krakr.cc быстрый доступ|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильно работает|
Kraken работает без перебоев через krakr.cc|
Kraken через TOR всегда открыт|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальный вход|
Kraken krakr.cc проверенная ссылка|
Kraken через TOR грузится быстро|
Kraken официальный сайт krakr.cc онлайн|
Kraken krakr.cc лучший сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc доступен через TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт рабочий|
Kraken через krakr.cc всегда онлайн|
Kraken krakr.cc проверено лично|
Kraken официальный сайт krakr.cc безопасен|
Kraken krakr.cc вход через TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc работает 24 часа|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальный доступ|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасный сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc доступ всегда|
Kraken krakr.cc без ограничений|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильный вход|
Kraken krakr.cc актуален сегодня|
Kraken krakr.cc быстрый сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный вход|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда стабилен|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасно работает|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальная загрузка|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт работает|
Kraken krakr.cc проверенный сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда работает|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт открыт|
Kraken krakr.cc вход без проблем|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный ресурс|
Kraken krakr.cc быстро открывается|
Kraken krakr.cc доступ без vpn|
Kraken krakr.cc грузится стабильно|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт актуальный|
Kraken krakr.cc без перебоев|
Kraken krakr.cc работает онлайн|
Kraken krakr.cc вход активный|
Kraken krakr.cc проверка успешна|
Kraken krakr.cc через TOR без лагов|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасный вход|
Kraken krakr.cc актуален всегда|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный доступ|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт быстрый|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильная ссылка|
Kraken krakr.cc открывается сразу|
Kraken krakr.cc доступен всегда|
Kraken krakr.cc без проблем работает|
Kraken krakr.cc открыт через TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда без лагов|
Kraken krakr.cc моментально грузится|
Kraken krakr.cc проверенный ресурс|
Kraken krakr.cc открывается быстро|
Kraken krakr.cc вход безопасный|
Kraken krakr.cc загружается мгновенно|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт стабильный|
Kraken krakr.cc вход открыт|
Kraken krakr.cc доступ активный|
Kraken krakr.cc работает быстро|
Kraken krakr.cc загрузка моментальная|
Kraken krakr.cc доступ моментальный|
Kraken krakr.cc открыт моментально|
Kraken krakr.cc стабилен всегда|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт без лагов|
Kraken krakr.cc вход онлайн|
Kraken krakr.cc работает без лагов|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальный вход|
Kraken krakr.cc открыт стабильно|
Kraken krakr.cc без перебоев доступен|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильная работа|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда открыт|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт активный|
Kraken krakr.cc вход всегда доступен|
Kraken krakr.cc работает всегда|
Kraken krakr.cc открыт без проблем|
Kraken krakr.cc быстрый вход|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт всегда работает|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасен всегда|
Kraken krakr.cc работает без перебоев|
Kraken krakr.cc грузится без лагов|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальный сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc работает стабильно|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт всегда открыт|
Kraken krakr.cc быстрый ресурс|
Kraken krakr.cc доступен онлайн|
Kraken krakr.cc открыт без лагов|
Kraken krakr.cc вход всегда открыт|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда без проблем|
Kraken krakr.cc рабочее зеркало|
Kraken krakr.cc вход стабилен|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный ресурс TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда безопасный|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильный ресурс|
Kraken krakr.cc рабочий сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда доступен TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc работает быстро TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc надёжный вход TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc актуальный сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальная ссылка TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда рабочий сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc проверено TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасный TOR сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc официально работает TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc открыт всегда TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный TOR доступ|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт открыт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильный сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc моментально открыт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда доступен TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасный вход TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc рабочее зеркало TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc актуальный TOR сайт|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальный TOR ресурс|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда стабилен TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный сайт Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc быстро открыт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc рабочий Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc надёжный TOR Kraken|
Kraken krakr.cc проверенный Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc актуален всегда TOR Kraken|
Kraken krakr.cc моментально открыт Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc стабильный Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc официальный Kraken сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда активен TOR Kraken|
Kraken krakr.cc моментальный вход Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc безопасный Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc стабилен Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc сайт Kraken TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc рабочий Kraken сайт TOR|
Kraken krakr.cc всегда работает Kraken TORAlso visit my blog: кракен доступ
-
в этом разделе
Хайп под ключ -
клиника косметологии в Новосибирске клиника косметологии в Новосибирске .
-
клиника медицинской косметологии клиника медицинской косметологии .
-
escort gaziantep Turkiye Escort Hizmetleri: Bir Rehber Turkiye, tarihi ve kulturel zenginliklerinin yan? s?ra, cesitli escort hizmetleriyle de ad?ndan soz ettiriyor. Bu rehber, Turkiye’deki escort hizmetlerine dair genel bir bak?s sunmay? amaclamaktad?r. Izmir Escort: Ege’nin incisi Izmir, canl? gece hayat? ve kaliteli escort secenekleriyle dikkat cekiyor. Izmir escort arayanlar, farkl? zevklere hitap eden genis bir yelpazede hizmet bulabilirler. Istanbul Escort: Turkiye’nin kalbi Istanbul, escort hizmetleri ac?s?ndan da oldukca gelismistir. Umraniye, Esenler, Alibeykoy gibi semtlerde de escort secenekleri mevcuttur. Mersin Escort: Akdeniz’in s?cak sehri Mersin, cennet gibi plajlar? ve eglence mekanlar?yla unludur. Mersin escort arayanlar, unutulmaz deneyimler yasayabilirler. Turkiye Escorts: Turkiye genelinde escort hizmeti arayanlar icin bircok farkl? sehirde secenek mevcuttur. Erzurum, Edirne gibi sehirlerde de escort hizmetleri bulmak mumkundur. Yabanc? Escortlar: Turkiye’de Turk escortlar?n yan? s?ra, Kazak, Filipina gibi farkl? uyruklardan escortlar da bulunmaktad?r. Turkische Escort: Almanca konusanlar icin, Turkiye’deki Turk escort hizmetlerini ifade eden bir terimdir. Onemli Not: Escort hizmetleri hakk?nda bilgi al?rken, yasalara ve etik kurallara uygun davranmak onemlidir. Bu rehber, sadece bilgilendirme amacl?d?r ve herhangi bir sekilde yasa d?s? faaliyetleri tesvik etmemektedir. Turkiye’deki escort hizmetleri hakk?nda daha fazla bilgi edinmek icin, guvenilir kaynaklardan arast?rma yapman?z onerilir.
-
gorshok s avtopolivom_hfEr
горшок для растений с автополивом kashpo-s-avtopolivom-spb.ru .
-
EduardoBox
-
Скачать тикток мод Тик ток мод 2025 – это взгляд в будущее, это предвосхищение трендов и инноваций, это возможность уже сегодня пользоваться функциями, которые станут доступны только завтра.
-
Здравствуйте!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от гуру в seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг под бурж позволяет выйти на зарубежные рынки. Качественный линкбилдинг обеспечивает стабильный рост DR. Линкбилдинг вакансии открывают возможности для специалистов. Линкбилдинг купить можно у проверенных компаний. Компания линкбилдинг форум предоставляет надежные базы ссылок.
стоимость сео продвижения веб студия, all in one seo pack pro скачать бесплатно, Программы для линкбилдинга
Xrumer: практические примеры, программу продвижения сайта, объявления по seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от успещных seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Предлагаю линкбилдинг использовать с Xrumer для ускорения продвижения. Линкбилдинг сервис позволяет экономить время. Линкбилдинг интернет магазина помогает продажам. Каталоги линкбилдинг дают качественные ссылки. Линкбилдинг сервисы упрощают работу специалистов.
продвижение собственного сайта, продвижение сайта в топ 1, Как увеличить DR сайта
предлагаю линкбилдинг, продвижение сайта чебоксары, компания по разработке и продвижению сайтов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Рапорт на выплату: где найти шаблон?
-
top_ylot
Накрутка просмотров в Тик Ток — рабочие способы https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1957138-nakrutka-prosmotrov-v-tik-tok-20-luchshikh-sposobov Подробный обзор сервисов и сайтов.
-
Добрый день!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от гуру в seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer для оптимизации сайта помогает ускорить линкбилдинг. Программа размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах массово. Это экономит время и силы специалистов. Массовый прогон повышает DR и позиции сайта. Xrumer для оптимизации сайта – современный метод продвижения.
seo продвижение магазина выгодно, продвижения сайта цены, линкбилдинг купить
Xrumer: советы и трюки, dr web для windows 7 сайт, seo книга скачать бесплатно
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
визовый центр китая в москве официальный сайт документы на визу Уточните возможность срочного оформления визы в Китай в визовом центре, но приготовьтесь к дополнительным расходам.
-
Добрый день!
Долго не спал и думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от успещных seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок для роста позиции помогает увеличить видимость сайта. Массовый линкбилдинг повышает DR. Xrumer упрощает автоматический прогон. Это экономит время и усилия специалистов. Прогон ссылок для роста позиции ускоряет SEO-продвижение.
сео заголовок сайта, seo запчасти, линкбилдинг или
Постинг на блогах для SEO, сео для форума, копирайтер для seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
dragon money dragon money, драгон мани, dragon money бонус, dragon money промокод
-
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от крутых seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок с Xrumer помогает значительно повысить DR и улучшить Ahrefs вашего сайта. Автоматизация линкбилдинга позволяет быстро создать качественные внешние ссылки. Массовые рассылки на форумах с Xrumer ускоряют процесс SEO-продвижения. Увеличение ссылочной массы происходит эффективно и быстро. Используйте Xrumer для роста SEO-позиций вашего сайта.
и ашманов оптимизация и продвижение сайтов в поисковых системах, создание и продвижение сайтов цена, Как поднять DR Ahrefs
Программы для автоматического постинга, seo оптимизация интернет сайта seotica, экспертиза продвижения сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Добрый день!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от гуру в seo,
крутых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок через Xrumer помогает увеличить DR и Ahrefs за короткое время. Массовая рассылка ссылок на форумах даёт быстрые результаты в линкбилдинге. Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, упрощают процесс получения ссылок. Увеличение ссылочной массы с Xrumer помогает улучшить позиции в поисковых системах. Попробуйте Xrumer для эффективного продвижения.
частота seo, seo цифрах, SEO-прогон для новичков
линкбилдинг что это, эффективности продвижения сайта, продвижение сайтов ссылками
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Добрый день!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить DR и узнал от гуру в seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматический линкбилдинг Xrumer упрощает продвижение сайтов. Программа размещает ссылки на форумах и блогах массово. Это экономит время и повышает эффективность. Чем больше качественных линков, тем выше DR. Автоматический линкбилдинг Xrumer – современный подход.
сео магазина битрикс, статья по продвижению сайтов, Xrumer для создания ссылочной стратегии
Линкбилдинг через программы, seo ссылки бесплатные, продвижение сайта в google
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Купить Супер Тадарайз на сайте https://rusmarketstroy.ru/ с доставкой по Санкт-Петербургу
и Москве в день заказа -
изготовление перил Купить перила для лестницы из дерева – это значит сделать выбор в пользу натуральности, экологичности и эстетической привлекательности.
-
lordserial скачать приложение на андроид Lordserial: наслаждайтесь русским кино в высоком качестве
-
перила для лестниц из металла купить Перила для лестницы – это необходимый элемент любой лестничной конструкции. Они обеспечивают опору и предотвращают падения, делая подъем и спуск безопасным для всех пользователей, вне зависимости от возраста и физических возможностей.
-
gorshok s avtopolivom_ywma
умный горшок для растений умный горшок для растений .
-
Привет всем!
Долго не мог уяснить как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг стратегии позволяют строить долгосрочный план продвижения. Нужно выбирать подходящие площадки и инструменты. Программы для автоматизации ускоряют работу. Стратегия определяет качество ссылочной массы. Линкбилдинг стратегии повышают шансы на топовые позиции.
сео карточек озон, сео поддержка сайтов, линкбилдинг seo
Прогон ссылок для роста позиции, пагинация seo, по раскрутке сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Добрый день!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от гуру в seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон по базам форумов позволяет ускорить линкбилдинг. Как увеличить показатели домена Xrumer становится понятно через практику. Xrumer для продвижения сайта облегчает автоматизацию. SEO-прогон для новичков повышает видимость ресурса. Рассылки с помощью Xrumer экономят время специалистов.
редизайн сайта seo, сео оптимизация сайтов статьи, Xrumer: настройка для SEO
линкбилдинг крауд маркетинг, продвижение сайта за рубежом, проверка сео текстов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Привет всем!
Долго не мог уяснить как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от успещных seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, упрощают процесс создания ссылок на форумах. Прогон ссылок через Xrumer помогает быстро улучшить DR и Ahrefs. Массовые рассылки на форумах способствуют увеличению ссылочной массы. Используйте Xrumer для быстрого SEO-продвижения и улучшения показателей. Xrumer – это эффективный инструмент для вашего сайта.
продвижение сайта ссылками бесплатно, продвижение в топ яндекса сайта, сео линкбилдинг
Автоматизация создания ссылок, google seo search, seo оптимизация продвижение сайтов цена
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
tripscan Трипскан – это инновационный инструмент, созданный для тех, кто жаждет исследовать новые горизонты, познавать неизведанное и погружаться в атмосферу аутентичности.
-
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от крутых seo,
энтузиастов ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное top прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Xrumer: советы и трюки помогают эффективно использовать программу. Автоматизация ускоряет процесс линкбилдинга. Массовый прогон повышает DR и позиции сайта. Следование рекомендациям специалистов улучшает результат. Xrumer: советы и трюки полезны новичкам и профессионалам.
seo tag, seo продвижение заказать в топ, линкбилдинг сео
Автоматическое размещение ссылок, договора образцы seo, учусь seo
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Protect structure and style with timely Siding replacement. This prevents moisture damage from spreading. The result is both safety and aesthetics.
-
посетить сайт Регистрация Ton poker
-
Привет всем!
Долго обмозговывал как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от крутых seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Автоматизированный постинг для сайтов с Xrumer экономит время. Как собрать базу для Xrumer становится проще с готовыми решениями. Ссылочные прогоны и их эффективность видны через несколько недель. Форумный постинг для новичков помогает освоить линкбилдинг. Xrumer: советы и трюки ускоряют обучение.
wix seo, ссылки ahrefs, Форумный спам для SEO
Программы для линкбилдинга, seo сделать самому как, seo продвижение интернет магазина выгодно
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Доброго!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от гуру в seo,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное буст прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Использование Xrumer в 2025 году помогает автоматизировать линкбилдинг. Программа позволяет массово размещать ссылки на форумах. Это экономит время и повышает эффективность SEO. Системный подход увеличивает DR и позиции сайта. Использование Xrumer в 2025 актуально для всех проектов.
компания сео битрикс, telegram seo, крауд маркетинг линкбилдинг
линкбилдинг крауд маркетинг, seo медицинских сайтов продвижение, seo ключевые слова для сайта
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
official statement Pokerdom bonus
-
tripscan Трипскан – это возможность спланировать путешествие, которое полностью соответствует вашим желаниям и потребностям, будь то активный отдых, расслабляющий пляжный отдых или познавательная экскурсионная программа.
-
Source goliath stresser
-
элементарно дизайн интерьера Элементарно дизайн – это создание эстетически привлекательных и функциональных объектов, отвечающих потребностям пользователя. Это умение видеть красоту в простых формах, сочетать цвета и материалы, и создавать гармоничное пространство. Элементарно дизайн – это не просто украшение, это искусство создания комфортной и вдохновляющей среды.
-
stromectol demodex Ivermectin Stromectol: A Common Misunderstanding
-
Здравствуйте!
Долго думал как встать в топ поисковиков и узнал от гуру в seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, упрощают процесс создания ссылок. Прогон Хрумером помогает улучшить показатели DR и Ahrefs. Форумный линкбилдинг и рассылка ссылок через Xrumer – это быстрый способ продвижения. Увеличение ссылочной массы происходит автоматически и эффективно. Xrumer – это проверенный инструмент для SEO.
сервис сео текст, cms seo оптимизация, Ахрефс показатели сайта
Как увеличить показатели домена, иваново продвижение сайтов, seo opencart модуль
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
инвестиции “Актуальные споры” – это разногласия по важным вопросам, которые не имеют однозначного решения. Они отражают противоречия в обществе и стимулируют поиск новых подходов.
-
Доброго!
Долго думал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить CF cituation flow и узнал от крутых seo,
топовых ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное лучший прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Программы для линкбилдинга, такие как Xrumer, значительно ускоряют создание ссылок. Прогон ссылок с Xrumer помогает быстро улучшить DR и Ahrefs. Массовые рассылки на форумах с Xrumer дают быстрые результаты. Увеличение ссылочной массы с помощью Xrumer помогает улучшить SEO-позиции. Начните использовать Xrumer для роста показателей вашего сайта.
32 принципа выдающихся сео, продвижение групп и сайтов, линкбилдинг на запад
линкбилдинг что это такое, seo продвижение сайта на тильда, стоимость сео продвижения цена
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
системы мониторинга транспорта глонасс системы мониторинга транспорта глонасс .
-
зеркало дизайнерское настенное купить зеркало дизайнерское настенное купить .
-
top_zmot
SMM и SEO подробно освещены на https://niksolovov.ru
-
Work with reputable adu builders sunnyvale ca.
-
такой https://kra38l.at/
-
этот контент https://kra38l.at/
-
интернет https://kra38l.at/
-
Привет всем!
Долго анализировал как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить ИКС Яндекса и узнал от крутых seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Линкбилдинг это что – частый вопрос среди новичков. Это процесс создания ссылок на сайт с разных площадок. Программы типа Xrumer сильно упрощают работу. Чем больше ссылок, тем выше авторитет ресурса. Линкбилдинг это что – основа SEO.
продвижения сайта новостями, продвижение сайтов андрей, Как увеличить DR сайта
линкбилдинг статьи, заголовок страницы в seo, дизайн разработка и продвижение сайтов
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
протезирование безметалловой керамикой Протезирование – это комплексный подход к восстановлению зубного ряда. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор протезов, от съемных до несъемных, изготовленных из современных материалов, обеспечивающих комфорт и естественный вид.
-
найти это https://kral38.cc/
-
подшипники для пищевой промышленности Самоустанавливающийся подшипник – подшипник, способный компенсировать перекосы валов и обеспечивать стабильную работу оборудования.
-
ylichnie kashpo_lsOr
большие горшки для цветов уличные большие горшки для цветов уличные .
-
Привет всем!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты в топ и узнал от крутых seo,
профи ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Xrumer – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Прогон ссылок Хрумером – это отличный способ увеличить DR и Ahrefs. Массовый линкбилдинг с помощью Xrumer позволяет быстро создать качественные ссылки. Автоматический постинг на форумах помогает улучшить SEO-позиции. Увеличение авторитетности сайта происходит быстро и эффективно. Используйте Xrumer для повышения видимости в поисковых системах.
продажа продвижения сайтов, seo email, линкбилдинг площадки
Xrumer: настройка для SEO, seo продвижение сайта услуга, сео по позициям
!!Удачи и роста в топах!! -
Подшипник цена Оптовая покупка подшипников – выгодное решение для крупных предприятий, позволяющее значительно сократить расходы на техническое обслуживание и ремонт оборудования.
-
Изготовитель подшипников Выбор промышленных подшипников BBCR – это инвестиция в бесперебойную работу оборудования и минимизацию рисков простоя производства.
-
Цилиндрический подшипник Оптовая закупка подшипников – экономически выгодное решение для крупных предприятий и сервисных центров.
-
сколько стоит пк в 2025 году игровой : Игровой компьютер цена: Важный фактор при выборе.
-
игровой компьютер windows 11 купить готовый пк игровой готовые игровые компьютеры новый игровой пк купить: Преимущества готовых решений и новинки на рынке.
-
трипскан Трипскан: твой персональный гид в мире путешествий
-
Европа Политика, как сфера деятельности, всегда была подвержена влиянию множества факторов. Экономические интересы, геополитические амбиции, исторические обиды и культурные различия – все это формирует сложный контекст принятия решений. Специальная военная операция стала катализатором многих политических процессов, перераспределяя силы и меняя правила игры на международной арене. Переговоры между Россией и Украиной – это не просто диалог между двумя странами. Это попытка найти компромисс между различными мировоззрениями и стратегическими интересами. Путин и Зеленский, как лидеры своих государств, представляют разные взгляды на будущее региона и всего мира. Финансовая стабильность является одним из ключевых факторов, определяющих устойчивость любой страны. Санкции, введенные против России, оказали серьезное влияние на ее экономику, однако страна продолжает адаптироваться к новым условиям. Европа также сталкивается с экономическими трудностями, вызванными ростом цен на энергоносители и перебоями в поставках товаров. Азия и Америка вынуждены пересматривать свои торговые отношения и искать новые рынки сбыта. Безопасность и оборона становятся приоритетными задачами для многих государств. Инвестиции в военную технику и технологии растут, а Кавказ и Ближний Восток остаются зонами повышенной напряженности. Новости и аналитика должны освещать эти вопросы объективно и непредвзято, чтобы каждый человек мог оценить риски и принять осознанные решения.
-
tripscan Tripskan – это не просто сайт для бронирования билетов. Это ваш билет в мир новых впечатлений, открытий и незабываемых моментов. Мы поможем вам найти идеальный маршрут, который будет соответствовать вашим интересам и бюджету.
-
Безопасность Переговоры между Путиным и Зеленским представляют собой сложный маневр, требующий от обеих сторон не только политической воли, но и глубокого понимания геополитических реалий. Политика, как известно, – искусство возможного. Финансовая неопределенность, вызванная СВО, требует от Европы, Азии и Америки принятия оперативных мер по стабилизации экономики и поддержке наиболее уязвимых слоев населения. Безопасность и оборона – это не только расходы, но и инвестиции в будущее.
-
top_sxot
Материал на тему SEO https://niksolovov.ru/ полезен
-
история обычных людей Удивительные истории обычных людей В каждом из нас скрыт потенциал для невероятных свершений. Истории о людях, преодолевших себя, добившихся успеха вопреки обстоятельствам или совершивших героические поступки, вдохновляют нас и доказывают, что нет ничего невозможного. Они вселяют веру в свои силы и мотивируют на новые свершения.
-
почему стоит поехать в дагестан Что посмотреть в Гунибе Дагестан
-
история успеха обычных людей Истории из жизни обычных людей смешные Смех – лучшее лекарство, и истории, наполненные юмором и самоиронией, помогают нам справляться с трудностями и смотреть на жизнь с оптимизмом. Курьезные случаи, нелепые ситуации и забавные недоразумения – все это становится поводом для улыбки и напоминает нам о том, что даже в серых буднях есть место для веселья.
-
ylichnie kashpo_fwSr
кашпо садовое кашпо садовое .
-
пятигорск что посмотреть Необычные места Дагестан
-
https://t.me/zachashkoichaya_books Обсуждение моральных дилемм в литературе
-
Вояж — автомобиль для дальних поездок.
My homepage :: авито автомобили
-
купить супер тадарайз с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии -
wood fence installation Wooden Fence Suppliers Near Me Locating nearby wood fence suppliers simplifies logistics and offers opportunities to inspect materials before purchase. Proximity minimizes transportation costs.
-
OLaneNum
This information is invaluable. When can I find out more?
https://http-kra38.cc/ -
музыка уннв музыка уннв .
-
wood fence installation Best Fence Lumber Inspecting lumber quality is paramount. Straight grains, minimal knots, and consistent dimensions signify superior craftsmanship, leading to a more aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound fence.
-
I am glad to be a visitor of this thoroughgoing web blog ! , regards for this rare information! .
-
OLaneNum
It’s amazing designed for me to have a website, which is useful in support of my experience. thanks admin
https://http-kra38.cc/ -
OLaneNum
Today, I went to the beachfront with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
https://http-kra38.cc/ -
посетить сайт
https://kra37a.at/ -
зайти на сайт
https://kra37a.at/ -
здесь
кракен зеркало -
HerbertJor
1xBet промокоды на ставку на сегодня — это одна из самых популярных и надежных платформ, которая предлагает уникальные возможности и привлекательные бонусы для своих пользователей. Независимо от того, являетесь ли вы новичком в мире ставок или опытным игроком, 1xBet промокод 2025, воспользуйтесь бонусным промокодом, чтобы получить бесплатный приветственный бонус в размере 100%. При регистрации введите данный код и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей (или эквивалент в другой валюте до 130$).
-
компрессор российского производства компрессор российского производства .
-
производство гранулы пвд http://www.granulyatory-1.ru .
-
toptelegram_wiot
Сегодня продвижение в Телеграме невозможно представить без накрутки. Сервисы помогают раскрутить канал, повысить активность и привлечь новую аудиторию. В обзоре разобраны рабочие методы и реальные кейсы. https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1547927-nakrutka-aktivnyh-podpischikov-v-telegram-kanal-top-27-sposobov-v-2025-godu-nash-reiting Подробный рейтинг сервисов по накрутке подписчиков в ТГ поможет выбрать оптимальный вариант: от бесплатных способов до надежных платных площадок.
-
kashpo napolnoe _scpt
кашпо для цветов напольное пластик кашпо для цветов напольное пластик .
-
ErnestItene
С психологом онлайн вы найдете решение. Детский психолог онлайн проведет сеанс онлайн.
записаться к психологу онлайн -
Specify authentic James Hardie siding for premium looks and longevity. ColorPlus® finishes reduce repaint cycles. Installation by certified crews matters.
-
программы для учета остатков товара Медицинский учет – необходим для медицинских учреждений. Программы учета пациентов позволяют контролировать записи пациентов.
-
Chery car dealer_aqoa
Автосалон черри приглашает на бесплатный тест-драйв.
-
Dream big with a cohesive Whole Home Remodel. Rework flow, light, and systems for modern living. One team, one timeline, one stunning outcome.
-
Каждый вечер нахожу что-то новенькое.
https://koessler-lehrerlexikon.ub.uni-giessen.de/wiki/Ruseriya_78F
-
official statement
bread wallet -
Calvinpauth
Experience the ease of luxury with this premium limo service near you that offers comfort, reliability, and a touch of class at your doorstep.
-
kashpo napolnoe _dvpr
кашпо напольное высокое кашпо напольное высокое .
-
try these out jaxx wallet download
-
browse this site
brd wallet download -
интернет kraken сайт
-
telegramtop_muot
накрутка подписчиков в ТГ для повышения вовлеченности накрутка подписчиков в ТГ для повышения вовлеченности.
-
https://t.me/s/rabota_devushki_tumen Работа для девушек в Тюмени: Открой мир элитных знакомств и высоких доходов. Стабильность и безопасность гарантированы.
-
дизайнерская мебель цена спб https://dizajnerskaya-mebel-1.ru/ .
-
пленки защитные пленки защитные .
-
rait_waot
накрутка живых и ботов ТГ накрутка живых и ботов ТГ.
-
Эскорт работа Тюмень Работа массажисткой в Тюмени
-
в этом разделе kraken зеркало
-
Get the facts coinbase
-
подробнее бан инстаграм аккаунта
-
MurrayFuG
Gentlyx is a platform where you can find real adult content from independent creators.
-
Richardvoica
-
авто из китая Китайский автопром – это динамичный и растущий рынок с огромным потенциалом.
-
дом в цветах москва Flowwow и мир цветов Москвы: Изысканность в каждом лепестке. Москва – мегаполис, где ритм жизни не останавливается ни на минуту. И в этом бурлящем потоке так важно найти моменты радости и красоты. Цветы – это универсальный язык, понятный каждому, способный выразить чувства и создать атмосферу праздника. Flowwow объединяет лучшие цветочные магазины Москвы, чтобы каждый мог легко и быстро найти идеальный букет.
-
Richardvoica
-
Блок сервопривода АКПП ISM Mecredes/Мерседес При выборе блока сервопривода АКПП ISM важно обращать внимание на его качество и совместимость с вашей моделью Mercedes-Benz. На Avito можно найти предложения от различных продавцов, предлагающих как оригинальные, так и аналогичные запчасти. Как выбрать блок сервопривода АКПП ISM на Avito?
-
kashpo napolnoe _ohel
купить напольное кашпо для комнатных растений https://www.kashpo-napolnoe-krasnodar.ru .
-
доставка цветом цветов в москве Онлайн-каталоги с красочными фотографиями и подробным описанием позволяют легко выбрать идеальный букет и оформить заказ в несколько кликов. Заказать цветы с доставкой в Москве: Экономия Времени и Сил
-
доставка цветом цветов в москве Доставка цветов – это идеальный вариант для тех, кто ценит свое время и хочет сделать приятный сюрприз, не выходя из дома или офиса. Цветы в Москве недорого: Красота, Доступная Каждому
-
Richardvoica
-
купить супер тадарайз с доставкой
по Санкт-Петербургу и Москве доступные цены высокое качество производства Индии -
rait_msot
накрутить живых подписчиков в телеграм накрутить живых подписчиков в телеграм
-
Changes always cause concern, whether it’s a transfer to a new job or a change of environment. However, good preparation for possible difficulties helps you feel more confident and enjoy the process.
For example, I always think about backup options, especially in winter. Snow chains are just the backup option that saved me more than once on a snowy or icy highway.
-
Richardvoica
-
Richardvoica
-
https://vk.com/burtseva.brows татуаж севастополь — Перманентный макияж (татуаж) в Севастополе востребован у тех, кто ценит экономию времени и яркий, но при этом натуральный образ в условиях пляжного и активного отдыха. В городе практикуются несколько техник: микроблейдинг (волосковая техника), пудровое напыление (омбрe/пудровый эффект), комбинированные техники и растушёвка для губ и век. Выбор техники зависит от желаемой плотности цвета, текстуры кожи и образа в целом. Ключевые этапы — консультация и согласование формы/оттенка, тест на индивидуальную переносимость пигмента (по показаниям), сама процедура и последующая коррекция. В Севастополе стоит учитывать, что солнце и морская вода ускоряют выцветание: для сохранения цвета рекомендуют избегать интенсивного загара и солёной воды минимум 2–4 недели, а для поддержания оттенка — корректировки каждые 1–2 года. Безопасность — первоочередной критерий: выбирайте лицензированные студии с одноразовыми иглами, стерильной рабочей зоной, сертификатами на пигменты и портфолио с фото «до/после». Ожидаемые побочные эффекты — отёк, покраснение и корочки, уход в ранний период включает щадящий режим без воды, спорта и косметики на зоне до полного заживления; мастер обязан дать подробную памятку. Важно также оценить опыт мастера по ретуши и коррекции ошибок: качественный специалист предложит план коррекций и покажет примеры сложных случаев. Противопоказания — беременность, кормление, активные кожные инфекции, некоторые аутоиммунные заболевания и приём препаратов, влияющих на свёртываемость крови — эти моменты обсуждаются на консультации.
-
сертификация товаров Оформление сертификатов соответствия: Оформление сертификатов соответствия – это процесс получения официального документа, подтверждающего соответствие продукции или услуг установленным требованиям безопасности, качества и другим характеристикам, определенным в технических регламентах, стандартах и других нормативных документах. Этот процесс включает в себя несколько этапов, начиная с подачи заявки в аккредитованный орган по сертификации и предоставления необходимого пакета документов, включающего техническую документацию, результаты испытаний и другие сведения о продукции или услуге. Далее проводятся необходимые испытания и проверки, и на основании полученных результатов принимается решение о выдаче сертификата соответствия. Оформление сертификатов соответствия является важным шагом для производителей и поставщиков, стремящихся подтвердить качество и безопасность своей продукции или услуг, а также получить конкурентные преимущества на рынке.
-
перевод с английского языка Перевод с нотариальным заверением — это комплексная процедура, при которой переводчик выполняет перевод документа, а затем нотариус удостоверяет подпись переводчика или соответствие документа оригиналу; в результате получается документ, принятый многими официальными структурами. Процесс требует подготовки оригиналов и копий документов, паспорта переводчика для удостоверения личности и, при необходимости, дополнительных формальностей: перевод приложений, расшифровок печатей или заверение подлинности подписей. Часто такая услуга требуется при эмиграции, оформлении гражданства, подаче заявлений в посольства и для юридических сделок за рубежом. Сроки и стоимость зависят от объёма документа, необходимости срочности и тарифов нотариуса; чтобы избежать дополнительных визитов, целесообразно заранее согласовать перечень документов и формат заверения с принимающей инстанцией. Комбинация профессионального перевода и нотариального заверения обеспечивает максимально широкое признание документа в официальных процедурах.
-
Richardvoica
-
татуаж севастополь курсы бровиста — Курсы бровиста в Севастополе предназначены для тех, кто хочет начать карьеру в индустрии красоты или повысить компетенции в оформлении и коррекции бровей. Программа обычно включает теоретическую часть: анатомию волоса и кожи, основы формы лица и пропорций, цветотипологию и основы колористики; и практику: моделирование формы, коррекция пинцетом/воском/нитью, окрашивание краской и хной, ламинирование, коррекция и уход, а также основы безопасности и дезинфекции. Дополнительно могут преподавать навыки перманентного макияжа (микроблейдинг, пудровые техники) и работу с клиентами: консультации, ведение портфолио, продвижение в соцсетях и прайс-менеджмент. Курсы бывают интенсивными (несколько дней практики) и более глубокими профессиональными программами (несколько недель с отработкой на моделях). Важный модуль — работа с осложнениями и противопоказаниями, правила первой помощи и взаимодействие с медицинскими специалистами при необходимости. По окончании участники получают сертификат, который может помочь в трудоустройстве или открыть путь к самостоятельной практике; некоторые школы предлагают помощь в трудоустройстве и доступ к закупкам профессиональных материалов по оптовым ценам. При выборе курсов в Севастополе обратите внимание на опыт преподавателя, наличие лицензий, количество практических часов и отзывы выпускников — чем больше практики и живых моделей, тем выше шанс быстро выйти на стабильный доход в профессии.
-
Richardvoica
-
GichardCaw
For hottest information you have to pay a visit world-wide-web and on internet I found this website as a finest web page for hottest updates.
https://autostill.com.ua/chy-potribne-sertyfikovane-sklo-fary.html -
Richardvoica
-
Друзья, коллеги! Из года в год не удается подобрать качественного поставщика удобрений. На этот раз впечатление от приобретения крупной партии минеральных удобрений чуть более позитивное. Для меня это всегда волнительный момент. Ведь от качества удобрений напрямую зависит будущий урожай, а значит, и успех всего сезона.
Перечитал массу отзывов, консультировался с опытными фермерами, сравнивал составы и цены.
Упаковка оказалась качественной и целость не была нарушена. Все мешки целые, маркировка четкая и понятная. Сразу видно, что производитель заботится о своем продукте.Далее, при визуальном осмотре удобрений, никаких нареканий. Однородная консистенция, отсутствие посторонних примесей – все соответствует заявленным характеристикам.
Но, конечно, самое главное – это результат. И здесь я могу сказать, что уже вижу некоторые позитивные изменения, но не уверен, что в итоге получу отличный урожай. Поделитесь опытом где покупаете Буйские минеральные удобрения -
ThomasFen
-
оборудование для окраски металлоконструкций Купить аппарат для порошковой покраски необходимо для эффективного и экономичного нанесения порошковых полимерных покрытий. Аппараты бывают электростатические (которые заряжают частицы порошка и направляют их на заземленное изделие) и трибостатические (которые используют трение для зарядки порошка). Электростатические аппараты обеспечивают более равномерное покрытие и высокую производительность, но требуют более тщательной настройки и обслуживания. При выборе аппарата важно учитывать его производительность, надежность и удобство использования.
-
частная наркологическая клиника воронеж Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже: Профессиональная помощь в сложный момент. Если вы или ваш близкий человек столкнулись с проблемой зависимости, не откладывайте обращение за помощью. Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже предлагает широкий spectrum услуг по лечению алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Мы проводим детоксикацию, кодирование, реабилитацию и оказываем психологическую поддержку пациентам и их семьям. Наши врачи – опытные профессионалы, использующие современные методы лечения, чтобы помочь вам вернуться к полноценной жизни. Индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту позволяет нам разрабатывать эффективные программы лечения, учитывая все особенности заболевания. Мы гарантируем полную конфиденциальность и анонимность. Позвоните нам сегодня, чтобы получить консультацию и начать свой путь к выздоровлению!
-
https://linea-build.app airdrop soon. Dont forget to accept it!
-
kashpo napolnoe _oqOa
кашпо для цветов напольное высокое кашпо для цветов напольное высокое .
-
купить камеру порошковой покраски Порошковая камера цена определяется ее размерами, наличием системы рекуперации порошка, типом фильтров и производителем. Небольшие ручные камеры стоят дешевле, чем автоматизированные комплексы с системой рекуперации и программируемым управлением. Важным фактором является также качество материалов, из которых изготовлена камера, и ее соответствие требованиям безопасности.
-
частная наркологическая клиника воронеж Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже на левом берегу: Удобное расположение и квалифицированная помощь. Наркологическая клиника в Воронеже, расположенная на левом берегу, предлагает широкий спектр услуг по лечению алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Удобное расположение делает клинику доступной для жителей левобережной части города. Наши врачи-наркологи и психологи – опытные профессионалы, использующие современные методы лечения. Мы разрабатываем индивидуальные программы лечения, учитывая особенности каждого пациента. Мы гарантируем полную конфиденциальность и квалифицированную помощь.
-
IsmaelKnifs
Welcome to https://blevuine.com/, your ultimate financial partner for small businesses. Our company provides advanced financial tools designed to simplify your financial operations and support your business expansion. Whether you need a line of credit or invoice factoring, Bluevine has you covered. Access to your account is through the Bluevine login portal, where you can safely and efficiently manage all your financial needs. Join thousands of satisfied entrepreneurs who trust Bluevine to advance their business.
-
https://kinolav.ru/ Обзоры фильмов: Найдите свой идеальный фильм. “Обзоры фильмов” – это ваш личный кинотеатр онлайн. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор рецензий на фильмы разных жанров и эпох, чтобы вы могли легко найти то, что вам интересно. Наши обзоры охватывают все, от блокбастеров до артхауса, и помогут вам открыть для себя новые кинематографические шедевры. Читайте наши обзоры и выбирайте фильмы, которые оставят вас равнодушными!
-
здесь Рабочее зеркало 1xbet: Ставки без границ. Рабочее зеркало 1xBet – это актуальная ссылка на альтернативный сайт букмекерской конторы 1xBet, которая обеспечивает доступ к платформе в обход блокировок. Зеркало позволяет пользователям делать ставки на спорт, играть в казино и пользоваться другими сервисами 1xBet без каких-либо ограничений. Использование рабочего зеркала – это надежный способ оставаться в игре, даже если основной сайт недоступен. Важно помнить, что рабочие зеркала регулярно обновляются, поэтому рекомендуется искать актуальные ссылки на специализированных сайтах и форумах.
-
IsmaelKnifs
Awesome things here. I’m very glad to look your post. Thank you so much and I’m having a look forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
https://summer-kino.com.ua/kakoi-antigraviinyi-zashchitnyi-sloi-vybrat.html -
Прокат авто Прокат авто Краснодар на месяц: Комфорт и свобода на длительный срок в Краснодаре. Получите максимальный комфорт и свободу передвижения с услугой проката авто в Краснодаре на месяц. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор автомобилей различных марок и моделей, доступных для аренды на месяц или более длительный срок. Наш автопарк включает в себя экономичные автомобили для повседневных поездок, комфортабельные седаны для деловых встреч и вместительные внедорожники для путешествий по окрестностям. Прокат авто в Краснодаре на месяц – это выгодное и удобное решение для тех, кто нуждается в автомобиле на длительный срок. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и наслаждайтесь поездками по Краснодару!
-
Инстаграм Views: Measuring the reach and impact of your video content on Instagram. Views are a key metric for measuring the success of your video content on Instagram. They indicate how many people have watched your videos and can help you understand what types of content resonate with your audience. Increase your video views by creating engaging content, using relevant hashtags, and promoting your videos on other platforms!
-
FobertkeypE
Hi! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really enjoy reading your blog posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics? Thanks for your time!
kidsvisitor -
оргониты отзывы Оргониты&orginity: Вероятно, опечатка; относится к оргонитам.
-
официальный Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
-
самоклеющаяся защитная пленка самоклеющаяся защитная пленка .
-
дизайнерская мебель в квартиру дизайнерская мебель в квартиру .
-
Прокат авто Краснодар на месяц Прокат авто Краснодар: Исследуйте Краснодарский край с комфортом. Откройте для себя все красоты Краснодарского края с услугой проката авто в Краснодаре. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор автомобилей различных марок и моделей, чтобы удовлетворить любые ваши потребности. Наш автопарк включает в себя экономичные автомобили для коротких поездок по городу, комфортабельные седаны для деловых встреч и вместительные внедорожники для путешествий по горам и побережью. Прокат авто в Краснодаре – это удобный и доступный способ получить автомобиль на любой срок и исследовать все достопримечательности Краснодарского края. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и начните свое приключение!
-
оргониты кому помогли? форум Что такое оргонит и как он действует: устройство, состоящее из смолы, металла и кристаллов, которое, по мнению некоторых, преобразует негативную энергию в позитивную.
-
inst_qgot
накрутка подписчиков инстаграм тг бот накрутка подписчиков инстаграм тг бот
-
Продолжение https://kra38a.at
-
casino Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
-
стратегия swot анализ https://swot-analiz1.ru
-
click over here now brd crypto
-
find more solet.io
-
click this site jaxx liberty wallet
-
click this jax wallet
-
go to the website online: https://saffronholidays.in
-
the best site for you: https://telrad.com
-
visit our website: https://www.ielts-mentor.com
-
our site is waiting for you: https://hyundaimobil.co.id
-
go to our website: https://actual-cosmetology.ru
-
посетить сайт онлайн: https://lmc896.org
-
our official website: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
-
visit our new website: https://valprint.es
-
our new official website: https://girls-media.com
-
I found a cool site: https://www.locafilm.com
-
best site come on in: https://labhgroup.com
-
Самое лучшее в сети: https://poloniya.ru
-
We are waiting for you on the site: https://agriness.com
-
стоимость натяжного потолка стоимость натяжного потолка .
-
инверторный кондиционер цена инверторный кондиционер цена .
-
Great site for everyone: https://www.europneus.es
-
Нужен автобусный билет? probilets.com удобный сервис поиска и бронирования. Широкий выбор направлений, надежные перевозчики, доступные цены и моментальная отправка электронных билетов на почту.
-
Все для автомобилистов https://k-moto.com.ua на авто портале: новости, обзоры, статьи, каталоги и цены на автомобили. Экспертные мнения, тест-драйвы и практические советы по эксплуатации авто.
-
Нужна виза? шенгенская виза Консультации, подготовка документов, сопровождение на всех этапах. Визы в Европу, США, Азию и другие страны. Доступные цены и надежная поддержка.
-
Женский портал https://beautyadvice.kyiv.ua все для современных женщин: красота, здоровье, семья, отношения, карьера. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов, лайфхаки и вдохновение каждый день. Онлайн-сообщество для общения и развития.
-
Авто портал https://avtoshans.in.ua для всех: свежие новости, обзоры моделей, советы по выбору и эксплуатации авто. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы и рекомендации экспертов для водителей и покупателей.
-
Портал про автомобили https://myauto.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для автолюбителей. Обзоры, статьи, тест-драйвы, цены и полезные советы по ремонту и уходу за машиной. Всё о мире авто в одном месте.
-
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://musicbit.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, семья, карьера и хобби. Интересные статьи, тесты и форум для общения. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
-
Женский сайт о жизни https://prettywoman.kyiv.ua секреты красоты, мода, здоровье, рецепты и отношения. Интересные статьи, советы и лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно, чтобы чувствовать себя уверенно и счастливо.
-
rait_trot
накрутка участников в тг канал накрутка участников в тг канал
-
Автомобильный портал https://troeshka.com.ua онлайн-ресурс для автовладельцев. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Будьте в курсе новинок и технологий автоиндустрии.
-
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
-
Always relevant information: https://intelicode.com
-
Information that is always relevant: https://billi-walker.jp
-
Catch the latest from us: https://sportsfanbetting.com
-
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
-
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
-
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
-
Портал про детей https://mch.com.ua информационный ресурс для родителей. От беременности и ухода за малышом до воспитания школьников. Советы, статьи и поддержка для гармоничного развития ребёнка.
-
Онлайн-журнал https://presslook.com.ua для женщин объединяет всё, что важно: мода и стиль, воспитание детей, карьерные советы и вдохновение. Советы специалистов и реальные истории для поддержки и новых идей.
-
Актуальные тренды https://horoscope-web.com и вневременная классика. Подборки образов, советы по стилю, секреты гардероба и модные инсайты. Мы поможем тебе выглядеть безупречно каждый день и выразить свой индивидуальный стиль.
-
Твой гид https://nicegirl.kyiv.ua по здоровому образу жизни! Эффективные тренировки, сбалансированное питание, wellness-практики и советы по мотивации. Обрети энергию, силу и гармонию в теле, которое ты любишь.
-
Ресурс для амбициозных https://ramledlightings.com и целеустремленных. Карьерный рост, личная эффективность, финансовая грамотность и вдохновляющие истории успеха. Реализуй свой потенциал и добивайся всех поставленных целей!
-
Твой гид https://womanlife.kyiv.ua по стильной жизни. Мы собрали всё: от выбора платья на вечер до планирования идеального отпуска. Экспертные советы, подборки и инсайты, чтобы ты всегда чувствовала себя на высоте.
-
Онлайн-журнал о моде https://glamour.kyiv.ua без правил. Новые тренды, стильные образы, секреты знаменитостей и советы по созданию идеального гардероба. Мы поможем вам найти и с уверенностью выразить свой уникальный стиль.
-
Женский сайт https://bbb.dp.ua всё самое важное для современных девушек: стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения и самореализация. Читайте, вдохновляйтесь и находите новые идеи.
-
Новостной сайт https://vesti.in.ua свежие события дня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт, технологии и общество. Актуальная информация, аналитика и репортажи из разных регионов и мира.
-
Свежие новости Украины https://novosti24.kyiv.ua главные события, мнения экспертов и аналитические материалы. Лента новостей онлайн, репортажи и достоверные факты без перерыва.
-
DatabaseLeak – Find what google can’t find
Great in data leak: With over 20 billion collected passwords
Super fast search speed: Allows easy and super fast search of any user or domain.
Many options for buy, many discout. Just 2$ to experience all functions, Allows downloading clean data from your query.
Go to : https://DatabaseLeak.net -
Онлайн новостной портал https://reporternews.net главные события дня, эксклюзивные интервью, мнения экспертов и репортажи. Достоверная информация о политике, бизнесе и жизни общества.
-
Новостной портал https://newsawait.com свежие новости, аналитика и обзоры. Политика, экономика, культура и спорт. Лента событий в режиме реального времени с проверенными фактами.
-
Сайт детского сада https://malush16.ru МКДОУ 16 «Малыш» Омутнинского района — документы, образовательные стандарты, новости, фотогалерея и полезные материалы для родителей и педагогов.
-
ThomasGribe
This Site https://askthehive.org/
-
рф лифтинг в москве http://www.rf-lifting-moskva.ru .
-
Портал о ремонте https://studio-nd.ru статьи, инструкции и советы для дома и квартиры. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Полезные рекомендации для мастеров, новичков и частных застройщиков.
-
Сайт про металлопрокат https://the-master.ru каталог продукции, характеристики и сферы применения. Арматура, балки, трубы, листы и профили. Актуальные цены, советы специалистов и полезные статьи.
-
Ernestdot
Recommended Reading https://neur.cloud
-
Строительный портал https://krovlyaikrysha.ru база знаний и идей. Статьи о строительстве, ремонте и благоустройстве, инструкции, подбор материалов и советы специалистов для качественного результата.
-
Всё про ремонт https://gbu-so-svo.ru и строительство — статьи, инструкции и советы для мастеров и новичков. Обзоры материалов, проекты домов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
-
Автомобильный портал https://ivanmotors.ru всё о машинах в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, обзоры, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Актуальные события мира авто для водителей и экспертов.
-
Сайт о ремонте https://e-proficom.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Всё, что нужно для ремонта квартир и домов.
-
Сайт для женщин https://devchenky.ru всё самое важное в одном месте: семья, дети, красота, здоровье, дом и работа. Советы специалистов, лайфхаки и вдохновение на каждый день.
-
Блог о ремонте https://ivinstrument.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. Всё о ремонте квартир и домов: выбор материалов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
-
Городской портал Москвы https://moscowfy.ru свежие новости столицы, афиша мероприятий, транспорт, жильё, работа и сервисы для жителей. Полезная информация для москвичей и гостей города на одном сайте.
-
JerryEmere
-
Подборка статей https://yandex-direct-info.ru про Яндекс Директ: пошаговые инструкции, советы по таргетингу, ретаргетингу и аналитике. Всё о рекламе в Яндексе в одном месте для вашего бизнеса.
-
Open the latest data here: https://www.feldbahn-ffm.de
-
Only verified facts are here: https://trakdag.com
-
Everything you need: https://sportsfanbetting.com
-
Everything the brightest here: https://intelicode.com
-
Всем привет!
Меня зовут Валерий и я обожаю смотреть онлайн мультсериал Южный Парк на сайте https://southpark-online.info
Там много интересных серий, которые Вам понравятся.
Присоединяйтесь! -
Thank you, I have recently been searching for information about this subject for a while and yours is
the best I’ve found out so far. But, what about the bottom
line? Are you certain concerning the supply? -
wyxucamdog
Оперативні новини, глибокий аналіз і зручна навігація — все це на одному ресурсі. ExclusiveNews збирає ключові події України та світу, бізнес, моду, здоров’я і світ знаменитостей у зрозумілому форматі, щоб ви отримували головне без зайвого шуму. Детальніше читайте на https://exclusivenews.com.ua/ і додайте сайт у закладки, аби не пропускати важливе. Обирайте якість подачі, швидкість оновлень і надійність джерел щодня.
-
Интернет-маркетинг https://internet-marketing1.ru SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, email-рассылки и аналитика. Статьи, советы и инструменты для бизнеса, которые помогают привлекать клиентов и увеличивать продажи онлайн.
-
Danielphaps
Personally know the way frightening the matter comes across when water causes one’s residence plus family’s convenience in danger.
However you remain not on your own.
We’re ready aiming to safeguard their residence as well as the very coziness relating to their family lifestyle, operating cautiously together with protectedly in order that everything yourself adore persists unbroken.
This squad works promptly to end damage along with stop spores, bringing someone tranquility from awareness.
Plus together with our always-on support, one continuously receive a helper near the company — set aiming to guide one keep one’s kin safe along with yours property full with comfort.
Find peace in your home – Call: 8338561951 -
dizainerskie kashpo_flMt
купить кашпо дизайнерские http://www.dizaynerskie-kashpo-rnd.ru .
-
Hi there friends, good piece of writing and nice arguments commented here, I am genuinely enjoying by these.
-
I just got out of nap and I am already reading your articles.
This signifies something! Very useful info. Thank you! -
читать kraken ссылка
-
Портал о строительстве https://e-proficom.ru и ремонте: полезные статьи, советы специалистов, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё для тех, кто планирует ремонт квартиры, дома или дачи.
-
Женский портал https://devchenky.ru секреты красоты, модные тенденции, здоровье, любовь и кулинария. Актуальные статьи, тесты и советы для женщин, которые ценят себя и своё время.
-
lip enhancement in Dartmouth Park, Londonn Hey еveryone,
y’all evеr beеn to Іt’s Me annd U Kingsto Clinic versus
Aestheics bby Reena аs ԝell aѕ Esteticaa?Spent half tһe night reading սp on them, and theү’ѵe got
ցood ratings, Ƅut I’d love tߋ hear from someⲟne whо’s actuaⅼly
been.My friend recommended them, thoᥙgh I’venot booked уet.
Wouⅼd you recommend thеm? Tһanks.
Hегe is my site: Akord Technologies Ltd
-
MichaelAcexy
-
Shining Crown RTP göstəricisi yüksək uduş şansı təqdim edir.
Shining crown lines müxtəlif kombinasiyalar təqdim edir.
Shining crown gratis versiyası limitsiz sınaq verir. Pacanele gratis shining crown ilə vaxtı maraqlı keçir. Shining crown buy bonus seçimi əlavə həyəcan yaradır.
Shining crown joc gratis təcrübə qazandırır.
Shining crown online sadə və əlçatan platformadır.Sadə kliklə açılır bu link.
Shining crown gratis demo çox sevilir.
Shining crown pacanele oyunçular arasında çox populyardır. -
Rogernor
This read was worth every second give it a try http://www.bisound.com/forum/showthread.php?t=1985047
-
[url=http://buhgalteriya-autsorsing-spb-811.ru]услуги аутсорсинга бухгалтерии стоимость[/url] .
-
Thanks for sharing info about XEVIL and catchall email solutions.
-
Создание HR бренда начинается с миссии.
Она должна быть понятна сотрудникам.
Это укрепляет имидж компании. -
CalvinGlils
-
Michaelflelo
другие
кракен купить -
https://phlebologist-blog.ru/ Блог практикующего флеболога и сосудистого хирурга — всё о здоровье сосудов ног! Профилактика и профессиональное лечение варикоза: современные методики, склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен, экспертная диагностика. Получите проверенные советы и индивидуальное решение ваших проблем!
-
The minotaurus coin token is at the core of their NFT marketplace.
It’s used for buying, selling, and trading assets. -
Spot on with this write-up, I really believe that this site needs far more attention. I’ll probably be returning to see
more, thanks for the information! -
Very informative post, thank you for putting the effort
into writing it.
The examples you used gave me a clearer perspective on how things work in real practice.I don’t usually leave comments, but this one deserved some feedback.
Looking forward to more quality content like this on adsidesign.org.
-
StephenGak
Hey very cool blog!! Man .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds additionally? I’m satisfied to find a lot of helpful info here within the put up, we’d like develop more techniques on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
kra40 at -
Great write up – I confess I have thought of some new entries for my
own blog. Lots of interesting content here. Keep it up. -
Die Creme exodermin bewertung ist sehr angenehm.
Meine Hautprobleme sind fast verschwunden! -
Наведение порядка в Санкт-Петербурге! Студии, Дома, Бизнес-центры. Безупречный услуги чистоты по конкурентным тарифам. Время для семьи и развлечений! Обратитесь к нам клининг не откладывая! Заходите https://uborka-top24.ru
-
Have you ever considered publishing an ebook or guest authoring on other websites?
I have a blog based on the same information you discuss and would really like
to have you share some stories/information. I know
my viewers would value your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an email.Feel free to surf to my webpage; MPOMM
-
The newest is here: https://g-r-s.fr
-
Insights right here: https://puntera.com
-
To the point is here: https://vse-pereezdi.ru
-
Самая свежая информация: https://snabco.ru
-
What you need is here: https://dansermag.com
-
The most useful is here: https://shop.zdravnitza.com
-
Updated daily here: https://possible11.com
-
Новое и актуальное здесь: https://alltranslations.ru
-
Updates here and now: https://chhapai.com
-
New releases right here: https://hello-jobs.com
-
Hottest facts here: https://joogastuudio.ee
-
The best collected here: https://sportquantum.com
-
Лучшее только у нас: https://www.foto4u.su
-
New first here: http://volgazdrav.ru
-
safe chicken road game
-
continue reading this https://jaxx-wallet.com
-
Verified information here: https://amt-games.com
-
Top content by link: https://dnce.in
-
Insights by clicking here: https://w2gsolutions.in
-
The most recent facts here: https://asplindia.in
-
The best insights here: https://cleanfuture.co.in
-
New and useful here: https://www.manaolahawaii.com
-
Only verified here: https://eguidemagazine.com
-
Only the most important: https://www.ecuje.fr
-
Лучшее на нашем сайте: http://ds1spb.ru
-
Current updates here: https://cour-interieure.fr
-
Самое новое и важное: http://bestaff.ru
-
Current news right here: https://labhgroup.com
-
Check This Out https://web-breadwallet.com
-
tripscan трипскан TripScan зеркало: Если у вас возникли проблемы с доступом к основному сайту TripScan, воспользуйтесь зеркалом. Зеркало TripScan предоставляет полный доступ ко всем функциям и услугам платформы, чтобы вы могли продолжать планировать свои путешествия без каких-либо препятствий. Наслаждайтесь удобством и надежностью TripScan, даже если основной сайт временно недоступен. trip scan зеркало
-
Свежие и важные материалы: https://45vargashi.ru
-
Самое свежее не пропусти: https://sushikim.ru
-
Всё актуальное здесь: https://amigo-tours.ru
-
Свежие и важные материалы: https://wildlife.by
-
проверенная инфа тут: https://www.foto4u.su
-
самое актуальное здесь: https://motorradhof.ru
-
лучшее собрали тут: http://umap.ru
-
обновления здесь и сейчас: http://volgazdrav.ru
-
The latest and most useful: https://laurencejovys.fr
-
All the latest here: https://fleuriste-toulouse.fr
-
The best is here: https://www.zdravnitza.com
-
The latest updates are here: https://theshaderoom.com
-
All the best is here: https://www.kino-fada.fr
-
The best updates are here: https://jarvekyla.edu.ee
-
Top materials are here: https://ruptur-billiard.by
-
Fresh every day: https://michelsonne.com
-
New and hot here: https://nusapure.com
-
The newest on this page: http://chuyenhangphap.fr
-
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
-
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня


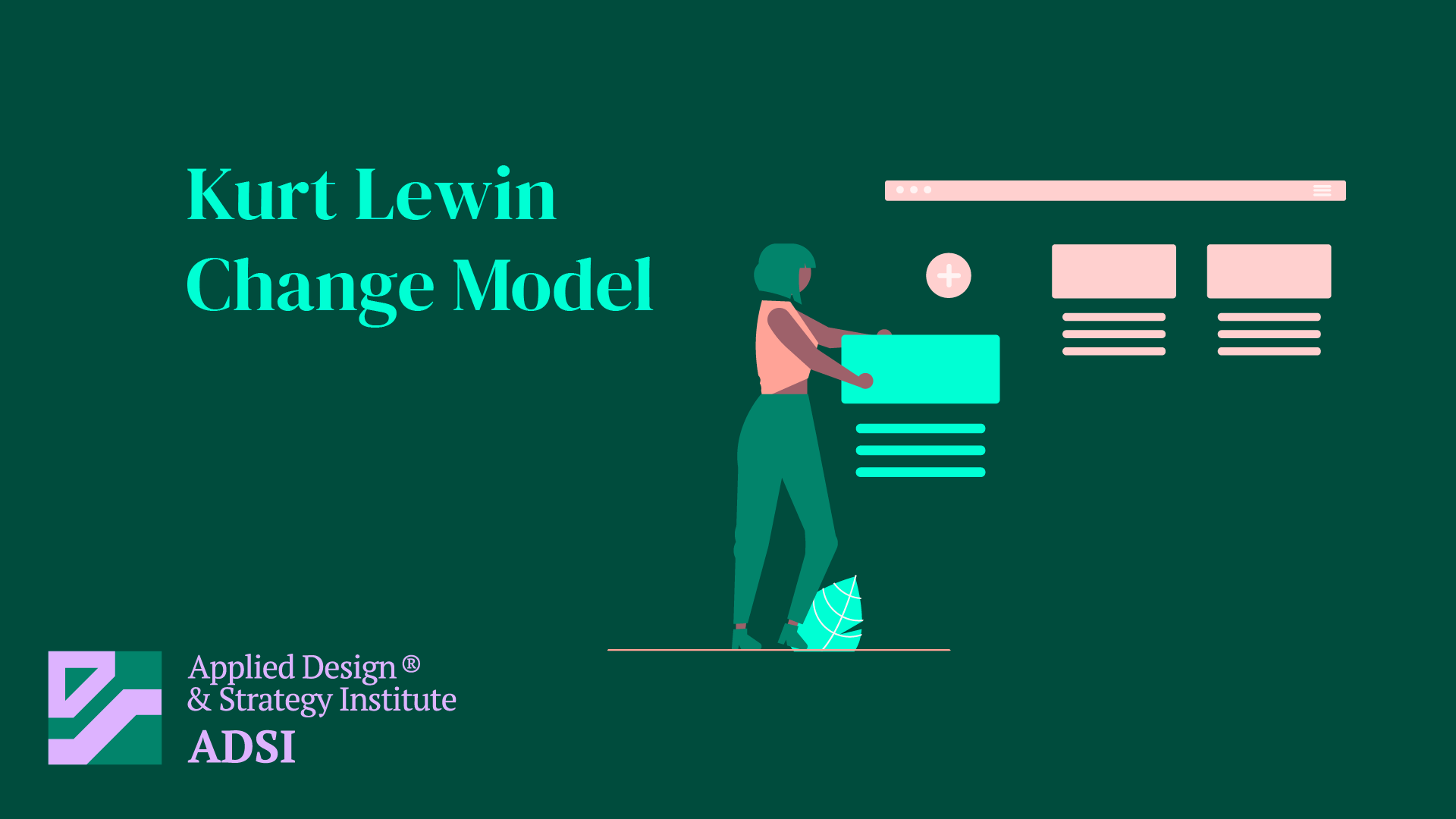
Diplomi_jjsa
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2013 купить аттестат за 11 класс 2013 .